Animals that have disappeared due to human fault. Rare and endangered animals. Animals of the black book
The last Tasmanian wolf - marsupial mammal with a dog's head - died in the Australian Zoo in 1936. And although for a long time It was believed that some unknown infection, which marsupial wolves allegedly contracted from dogs brought to Australia, was responsible for the disappearance of an entire species of animals; in fact, the responsibility for the extermination of this species of wolves lies entirely with humans.
Unfortunately, Tasmanian wolves are far from the only animal species that has been completely or partially destroyed by humans. Yes, in natural nature animals meet with a large number threats to their own existence - here are sudden climate changes, and predators who also need to eat something, and unexpected epidemics - but the biggest threat to the animal world has always been man with his ineradicable desire to kill. We have chosen 10 species of animals that have been exterminated by humans to show what we have lost.
(Total 10 photos)
Post Sponsor:
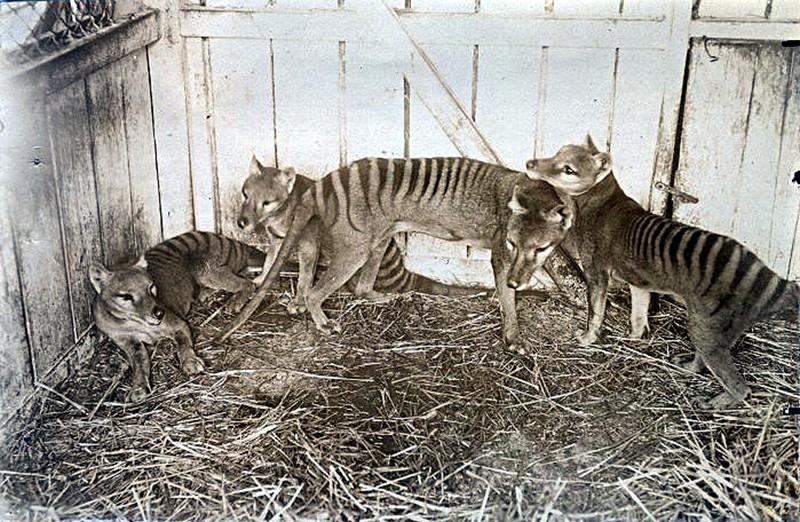

1. Tasmanian wolf
The Tasmanian or marsupial wolf, also known as the thylacine, lived on mainland Australia and the island of New Guinea. For the first time its habitat was changed after New Guinea Dingo dogs were transported by people. The latter forced the marsupial wolf out of its usual habitat, and in our time it “moved” to live on the island of Tasmania.
Local Australian farmers considered them a potential threat to their sheep and therefore mercilessly exterminated wolves, without paying any attention to where they saw them or whether they posed a threat to others.
“Many believe that the brutal and unjustified extermination of wolves could not lead to the complete extinction of an entire species of animals, and blame it on some unknown disease that allegedly wiped out the entire population of thylacines,” says Thomas Prowse of the Australian University of Adelaide.
However, scientists have studied this issue for a very long time and comprehensively, using various models, and discovered that man alone is responsible for the extermination of Tasmanian wolves.
It is believed that the last marsupial wolf was killed on May 13, 1930, and in 1936, the last marsupial wolf kept in captivity died of old age in an Australian zoo.
Year of complete disappearance: 1936
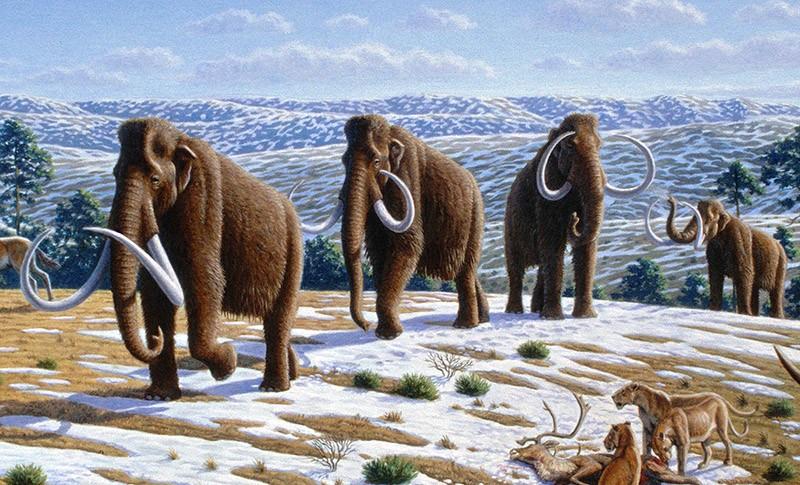

2. Woolly Mammoth
It is believed that this type of mammoth first appeared in Siberia about 300-250 thousand years ago and gradually spread to Europe and North America. The dimensions of mammoths were not as huge as most people not very familiar with history believe: they were only slightly larger than modern elephants.
Mammoths lived in groups, led by the eldest female, and constantly moved from place to place, since an adult mammoth required about 180 kilograms of food daily. Which - and this is obvious - does not involve marking time in one place.
Fully woolly mammoth disappeared about 10 thousand years ago. And while there are many theories about why they went extinct (loss of genetic diversity, climate change, outbreak, etc.), modern research They are increasingly inclined to believe that the final blow to this type of mammoth was dealt by the hand of man.
Time of complete extinction: 10,000 years ago
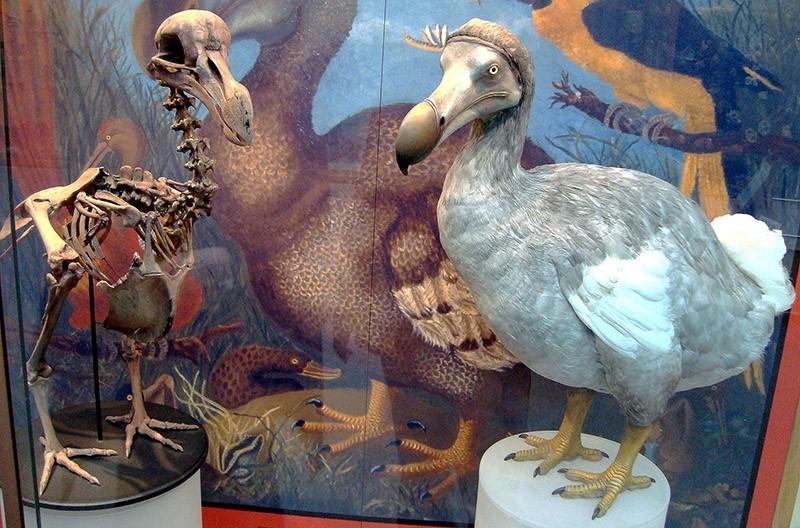

3. Dodo, or Mauritian dodo
The Mauritian dodo has long been considered a mythical bird whose existence was completely made up and did not actually exist in nature. But after specially organized expeditions to Mauritius discovered the remains of the bird, society had to accept the fact that the bird existed and it was people who caused its extermination.
The dodo lived in Mauritius for several centuries, completely without fear of its natural enemies, which simply did not exist on the island. That is why the bird was flightless - it simply had no one to hide from.
The bird was first seen in 1598 by Dutch sailors, and literally 100 years later it was completely exterminated - both the travelers themselves and the animals that the colonists brought to Mauritius tried. Just think for yourself how attractive a dinner from a 20-kilogram bird, the closest relatives of which are considered to be modern pigeons, was for sailors.
Year of complete disappearance: presumably 1681
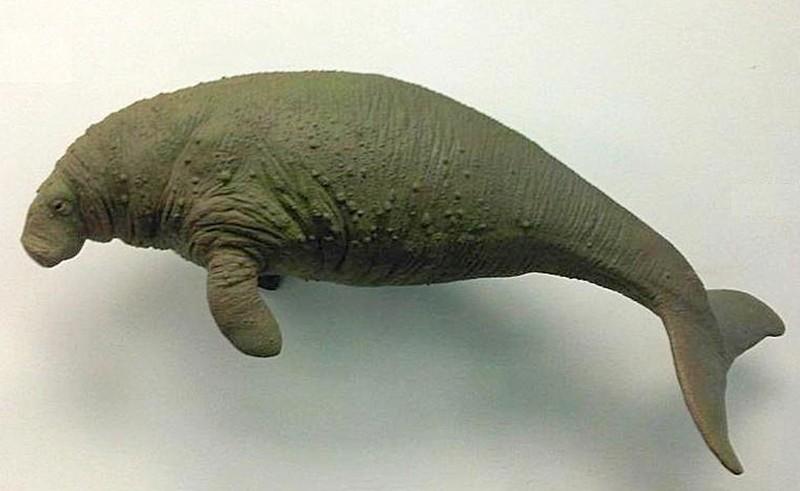

4. Sea cow
The sea cow or Steller's cow was discovered in 1741 by the expedition of Vitus Bering and received its name in honor of the expedition doctor Georg Steller, who was not too lazy to describe the sea cow from all sides, and it is his descriptions that are still considered the most complete.
Steller's cow lived off the coast of the Commander Islands and had not only low mobility, enormous size and complete absence fear of man, but also delicious meat. The latter was the reason that less than 30 years after its discovery sea cow was completely destroyed.
Sailors ate its meat, used cow fat for food and lighting, and made boats from the skin. In a word, they used everything they could get their hands on. At the same time, catching and killing sea cows was often unjustifiably cruel and senseless: “Often, hunters simply threw spears at a sea cow, and then let it swim away, hoping that the animal would die and its corpse would be washed ashore.”
Year of complete disappearance: 1768
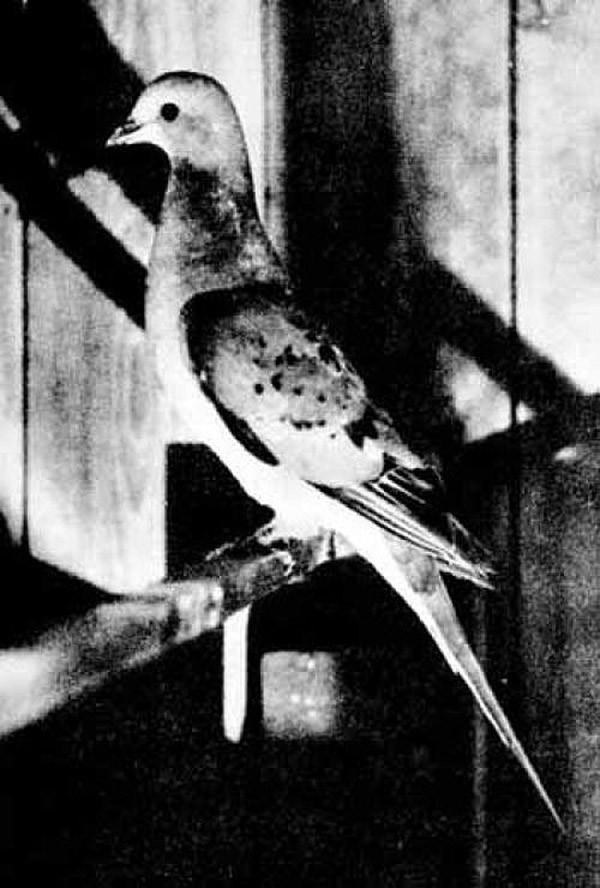

5. Passenger Pigeon
passenger pigeon before early XIX centuries, it was one of the most common birds on earth, its population numbered up to 5 billion individuals. However, this number of birds was not enough for the pigeons to survive. Passenger pigeons, which lived in the territory of modern USA and Canada, were the subject of active hunting by colonists arriving in America.
The decline in the number of pigeons took place at a more or less smooth pace until about 1870, after which in less than 20 years their numbers decreased simply catastrophically and the last pigeon in wildlife was seen in 1900. Passenger pigeons survived in captivity until 1914, when the last bird, named Martha, died at the Cincinnati Zoo.
Year of complete disappearance: 1914

6. North African cowbuck
Cow antelopes are a subfamily of large antelopes native to Africa. There are several species of them, but this particular species practically disappeared from the map of the Earth by the beginning of the 20th century. The hunting for them was so active that during the last few decades of their existence, cow antelopes were found only in truly inaccessible places in several African states, until they became completely extinct by the middle of the last century.
Year of complete disappearance: 1954
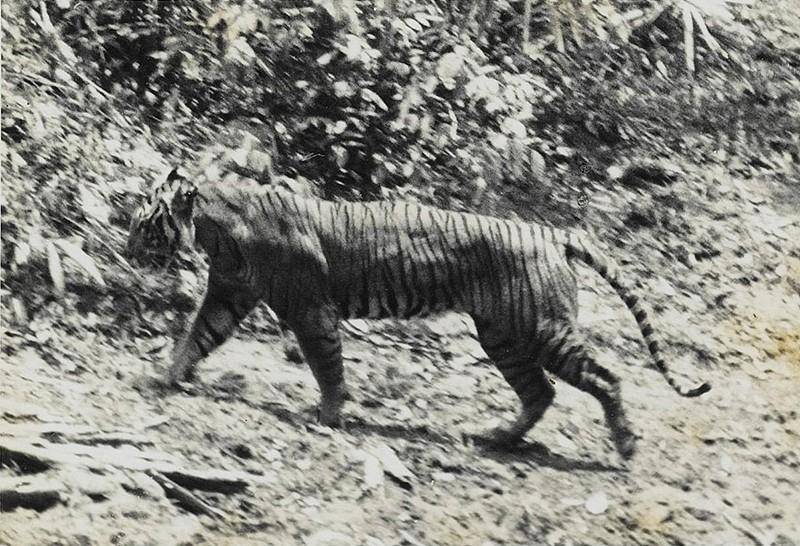

7. Javan tiger
Back in the 19th century, the Javan tiger was found throughout the island of Java and regularly annoyed its inhabitants. Maybe this was one of the reasons for the active hunt for it, or maybe something else, but the fact remains: by 1950, only 20-25 individuals remained alive on the island.
Moreover, half of these tigers lived in the territory of a specially created reserve. But even this was not enough to save the population, and by 1970 their number had dropped to seven individuals. Exact time The extinction of the Javan tiger remains unknown, but most likely occurred in the mid-1970s.
From time to time there are reports that a Javan tiger has been seen again in Java, or even a mother with several cubs, but there is no documented evidence that tigers have actually survived in the wild.
Year of complete disappearance: around 1970
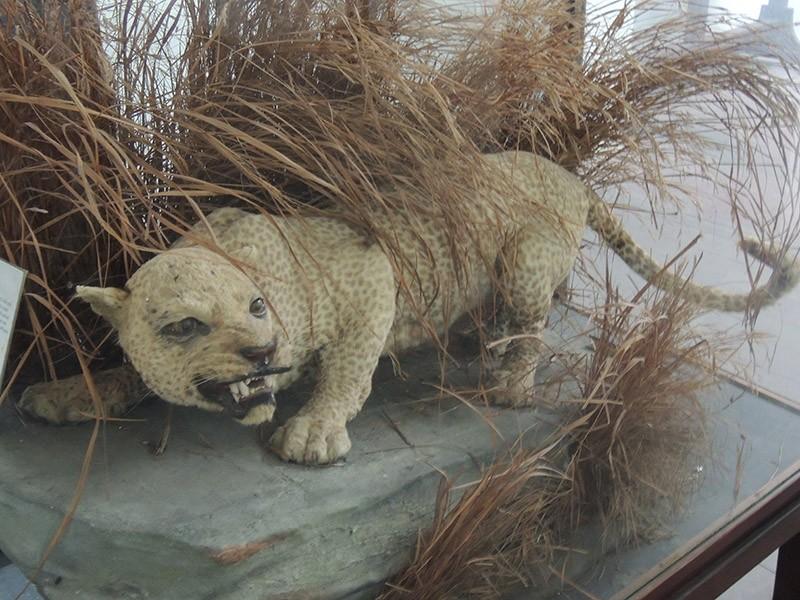

8. Zanzibar leopard
The extermination of the Zanzibar leopard is both similar and different from the extermination of other species on our list. They killed the leopard, they killed it purposefully and very actively, they declared a hunt for the animals and the whole village went after them. However, this was not done for the sake of its meat or skin, and not in order to protect the village and livestock from potential attacks by the animal. The fact is that the population of the Zanzibar archipelago was firmly convinced that these leopards were associated with witches, that evil witches specially bred and trained these animals to help themselves, and then sent the leopards to do dirty deeds for them.
The extermination campaign began in the second half of the 1960s, and after just 30 years there were almost no Zanzibar leopards left in the wild. Scientists began to sound the alarm in the early 90s of the last century, but a few years later the program to preserve the species was curtailed as unpromising.
Year of complete disappearance: 1990s
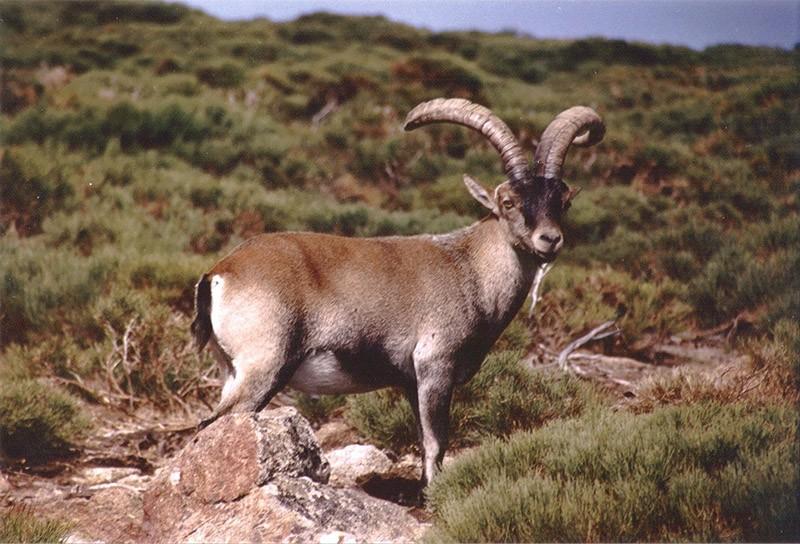

9. Iberian ibex
One of four known to science species of the Spanish wild goat, which, unlike the others, was not lucky enough to survive to this day. The last known representative of this species died a completely ridiculous death - he was crushed by a falling tree.
Scientists were able to take samples of its DNA and they attempted to create a clone of the ibex, but unfortunately, the cloned cub died shortly after birth due to various birth defects.
Year of complete disappearance: around 2000
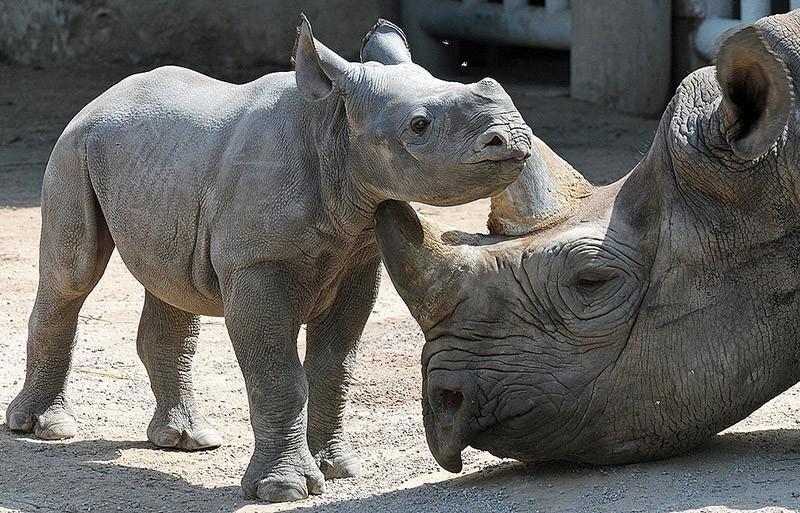

10. Western black rhinoceros
This subspecies of black rhinoceros was declared extinct just a couple of years ago. He became a victim of regular hunting in his habitat, in Cameroon. Rhino horns, used in Chinese medicine for the treatment of numerous diseases.
Scientists have been actively searching for surviving individuals of this species since 2006. However, since their search for five years was unsuccessful, the western black rhinoceros was declared extinct. Other species of black rhinoceros are also at risk of extinction.
Did you know that along with the famous Red Book, there is also a Black Book? This is a truly sad list, which includes already extinct species of animals and plants. And if we have hope (albeit weak) to preserve and even restore the number of populations from the Red Book, then we are no longer able to remove any species from the Black List. But how can we know that some animal has become extinct if we and none of our contemporaries have seen it? Based on bones found by paleontologists? But many of the fossil animals and plants are victims of their inability to adapt to changing conditions, in a certain sense - a dead-end branch of evolution. Is it possible to include dinosaurs, mastodons and mammoths in the Black Book? It turns out not. Although these animal species are already extinct. Read about the Red and Black Books of the world and Russia in this article.
Man and nature before the New Time: a fragile balance
Ancient people, especially during the Ice Age, lived by hunting. But, nevertheless, they did not cause significant damage to nature. There were a lot of animals, people's weapons remained too imperfect to bring rich trophies or catches. And homo sapiens as a species was not numerous at that time. People who lived at the dawn of civilization tried to adapt to natural conditions, and not modify them to suit your needs. They did not plow the land, did not cut down the forests and did not drain the swamps. They simply hunted, like wolves, lions and crocodiles do. Perhaps mammoths disappeared in the end ice age due to human fault. But they are not in the Black Book. Because only those extinct species of animals and plants that disappeared after 1500 are listed there. In the Middle Ages, people began to think about reducing the population of animals that were hunted. Lords and kings began to prohibit hunting in their forests. But such measures were taken for the sake of hunting, only in the future, when the number of game in the forest has been restored. But, in principle, before the New Time, nothing threatened existing populations. 
Why is 1500 a key reference date?
Before the discovery of America, and then Australia, Europeans had no idea about the existence of many species of animals and plants. Travelers who were the first to set foot on new lands made notes and sketches of previously unseen flowers, trees, birds and animals. But, unfortunately, together with the Europeans in tropical paradise a terrible danger has come. Entire populations began to disappear. And this trend has not disappeared even now. Why do animal species become extinct? People having firearms, can kill more game. But hunting is not the only reason for this. Colonists often brought with them so-called aggressive species European animals. They either exterminated endemics or laid claim to their food supply. Europeans began to actively develop new territories - primarily by cutting down forests, draining swamps, and plowing lands. With this economic activity, people have deprived endemics of their usual habitats. The first victims were species that existed in Australia and New Zealand. There were simply no predators on the Green Continent and the archipelago. As a result of evolution, many species of birds have appeared that have forgotten how to fly. They became easy prey for people, dogs and cats. So, we don’t know for sure what happened to the wildlife of the New World before 1500. But what happened later is only our fault. 
People realized the danger only in the nineteenth century. Attempts have been made to restore some species, but they have proven clumsy. Animals were bred in captivity, and a couple of individuals were crossed, and then their children. As a result, such offspring turned out to be nonviable. Thus, the last passenger pigeon (named Martha) died in the zoo in 1914. Zoologist Gerald Durrell changed that. He turned menageries into zoos, where animals were kept in an environment close to natural. For successful regeneration of the species, several pairs of unrelated individuals are necessary. Once there are quite a lot of them, you can already think about how to release some of them into natural environment habitat. And only after they successfully adapt, show the ability to obtain food on their own and give birth to healthy offspring, can we hope for the restoration of the species. However, even then these animals are considered “critically endangered” or “vulnerable”. 
Symbols of threatened species
But as for those on the Black List, we can only hope that the last representatives of the disappeared population have become more cautious and are hiding somewhere in the wilds of the Amazon basin or in the depths of the oceans. Geneticists have an idea to revive extinct animal species by implanting their preserved DNA into the egg of a female of a similar type. However, so far such attempts have not been successful. At the beginning of this millennium, the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) summed up a sad result: over the past five hundred years, eight hundred and forty-four species of plants and animals have disappeared from the face of the earth. In the list of the Union they are classified by the abbreviation EX (Extinct). These are the subjects of the so-called Black Book, which lists species that disappeared after the death of the last individual. This does not include animals and plants that became extinct before 1500 - mammoths and dinosaurs. The list of species that have disappeared in modern times is published on the first page of the Red Books of the world, continent, region, country. Animals and plants are then classified according to their risk level. Topping this list are EW (Extinct in the Wild). The abbreviation means that in some zoos around the world there are still one or two individuals living, but this species is no longer found in the wild. Next come CR (critically endangered), EN (endangered), VU - vulnerable. The classification is assigned depending on the number of individuals and how preserved the territories are. natural habitat. Rounding out the list are CD (species that are dependent on conservation efforts), NT (near vulnerable) and LC (little threatened). 
Is salvation possible?
The Red Book is not just a long list of endangered plant and animal species. This is the motivation of all humanity to make every effort to preserve the invaluable gene pool of the planet. Extinct species of animals - a photo of a sea cow, a stuffed animal of the last Carolina parrot, who died in 1918, and other evidence - serve as a reproach to us. But is it possible to save populations that are on the verge of extinction? Sometimes yes. Examples include Australian koalas, bison, and pandas. 
Rescue measures
In some countries, a species is considered extirpated, while in others there are still dozens or even hundreds of individuals. This is the situation with common brown bears in France. Animals are first raised in zoos. Then they are transferred to nature reserves. When there are enough of them, they are moved to their natural habitat. The main thing is not to delay salvation. There are now two turtles of the species Rafetus vietnamensis left in the world. But, judging by the fact that the female lays unfertilized eggs, her gentleman can no longer leave offspring. 
Black Book of the World
The very first animals to leave the earth were those that lived on isolated islands where there were no predators. Back in 1546, the rodents Plagiodontia ipnaeum and Quemisia gravis, endemic to the island of Haiti, disappeared. The reason for this was the destruction of natural habitats, as well as the introduction of ordinary ship rats, which occupied the ecological niche of the animals. A century later, the Black Book, which describes extinct animal species, was replenished with the blue-and-yellow macaw and the dodo Dodo. Man caused the greatest harm to nature in the nineteenth century. There are dozens of species that have disappeared forever. This includes sea cows, Mascarenotus owls, Steller's cormorants and many others. The quagga is especially worth mentioning. These zebra-like equids lived in South Africa and were domesticated by humans. In fact, it is the only domestic animal that has gone extinct. Quaggas had very sensitive hearing and were used to guard herds. But the Boers exterminated these animals for their skins. In 1878, the last quagga was killed.
Black Book of the Russian Federation
Fortunately, Russia has huge areas, and its Asian part is almost undeveloped. Therefore, there are practically no extinct animal species in the country. However, as a result economic activity Some plants have disappeared forever. People are actively draining swamps and developing water meadows in river floodplains. And if the flora has been preserved in the forests, the same cannot be said about the meadow vegetation. The Black Book of Russia is compiled by region. Thus, in the European part of the country you will no longer find star cladonia, Norwegian astragalus, or Barguzin wormwood. Beyond the Urals you can no longer find common heather, beautiful feather grass, black alder and lattice. But the Volga cinquefoil (Potentilla volgarica) appears in two Black Books at once - Russia and the world. 
Red Book of the Planet
What does the International Council for Conservation of Nature mean by classifying a species as EN (Endangered)? This means that such organisms are threatened with complete extinction. Why and on what basis does the IUCN make this conclusion? Firstly, when there are critically few representatives of a given species, and secondly, when the habitats of these organisms are under threat. Now that a severe fight against poaching is underway, the second reason prevails. Many people respond to the call of environmentalists to save orangutans or koalas, but not many understand that the survival of these species is directly related to the reservation of primary forests and providing these animals with an adequate food supply. Who is under threat and who does the Red Book care about? Endangered animal species, according to disappointing IUCN statistics, make up 40 percent of all currently known organisms. The genetic wealth of our planet is becoming scarcer. The rate of extinction is not slowing down, but increasing. Most species have been included in the Black Book only in the last 150 years.
Critically endangered
Here we will name only 10 endangered animal species on the planet. This is a grizzly bear. Huge bear once found from Alaska to Mexico. Now there are 50 thousand individuals left in Canada and the USA. This species appears in the Black Book of Mexico. The western gorilla is disappearing at a catastrophic rate. Over the past twenty years, the number of these primates has decreased by 45 percent. In addition to poaching and habitat destruction (deforestation), a huge risk factor is the Ebola virus, to which gorillas are extremely susceptible. Sumatran and Bornean orangutans occupy third and fourth positions. Despite all efforts to maintain small populations in national parks, the number of animals over the past 60 years has decreased by 80 and 50 percent, respectively. Risk factors include deforestation and the capture of cubs for resale. The black and Javan rhinos are critically endangered due to human superstition. All efforts by the authorities to protect species from poaching are ineffective. Since animal horn is recognized as an aphrodisiac in Chinese medicine, it is worth more on the black market than gold. Chimpanzees, like gorillas, are susceptible to fatal human diseases. These are also endangered species of animals. The list closes African elephant(in the Black Books of Gambia, Burundi and Mauritania), Galapagos sea lion and Grevy's zebra.
Endangered animal species in Russia
The government is taking a number of measures to restore numbers Amur tigers. However, poaching and migration of animals to China does not reveal the true number of individuals. The Przewalski's horse was saved from extinction, just like the bison and other endangered species in Russia. As for the Far Eastern leopard, this species is still critically endangered.
Why is species conservation important?
There are four reasons for concern. The genetic wealth of our planet is diminishing by 1-5 species per day! This, in addition to moral problems, creates destabilization of ecosystems. The extinction of one species threatens the existence of others. Rare and endangered species of animals are irreplaceable genetic material. Artemisia annua, for example, contains a substance from which an anti-malaria drug is made. If this plant disappears, humanity could face a pandemic of this terrible disease. When a species goes extinct, it can lead to uncontrolled growth of other populations (including pests).
The question of how to relate to the extinction of certain animal species began to be actively discussed only in the 20th century. It is thanks to the activation various kinds Ecologists, “green” activists and animal rights activists formulated the problem of the disappearance of certain species as something out of the ordinary. Until this point, the public had not thought about it, and extinct animals were seen as a natural result of wildlife. A similar opinion exists even now - but still the main trend is the perception of the disappearance of a particular species as a local biological tragedy.
Animals appear, animals disappear...
In fact, the accusations of a certain “ecological radicalism” leveled at numerous “green activists” by their opponents are not without logic. Because if the majority of conservationists and animal activists share evolutionary theory, then they must remember that one of its fundamental postulates is the principle of “survival of the fittest.” That is, the type of animal that survives is the one that is best adapted to the changed conditions. environment or managed to develop the necessary functions and mechanisms. Consequently, those animal species that were outsiders in this struggle are forced to vacate their biological niche, that is, to disappear.
A clear illustration of this thesis are examples of animal species that have become extinct over the past 500 years, whose existence has been recorded historical sources. Moreover, the reason for their extinction is often not directly, but indirectly related to human activity. Most often, such a sad fate befell endemic animals, that is, species living in a localized territory isolated from the rest of the world. With the advent of man and the circumstances accompanying him (animals or insects brought with him purposefully or accidentally; brought diseases; changed structure of the environment, and so on), living conditions changed, and the animals were unable to adapt to them and disappeared. Here are some similar examples:
- Paleopropithecus, or giant lemur, lived in Madagascar at the time the island was discovered by Europeans. Was different large sizes and weight. The species disappeared by 1658;

- giant fossa, one of the species of endemic predators, Madagascar civets. This species disappeared at the same time as giant lemurs, and this is not a coincidence at all - lemurs were the main type of food for these large predators by local standards;

- The Mauritian ground goose is a representative of the duck family that lived on the island of Mauritius. Known since the middle of the 17th century and characterized especially at a fast pace Disappearance: Only twelve years passed when the colonists began to report in their letters that the numerous Ground Goose had practically disappeared. It is believed that the main role was played by rats and pigs brought by Europeans, who actively destroyed goose nests with eggs located on the ground.

Animals made extinct by humans
We cannot take away the impressive arguments from environmentalists, who do not miss the opportunity to blame humanity for the disappearance of one or another animal species. Over the past few centuries, human exploitation natural resources really acquired a previously unprecedented predatory character. A direct consequence of this was the disappearance of the range of animals. Let's remember some of them:
- the most famous example of this kind, which has become a symbol of the struggle to preserve rare species, is the Mauritian dodo. When Europeans arrived on the island of Mauritius, the first of whom were the Portuguese, the dodo was a numerous endemic species of flightless bird, distributed everywhere. They had no natural enemies, so they were very trusting of people. Portuguese sailors, who needed to replenish their meat supplies, took advantage of this by simply stunning the bird that came close to them with sticks. It was the Portuguese who gave the dodo the second name “dodo,” which translated means “stupid, fool.” Naturally, with such a disposition, the dodos in Mauritius were exterminated in the shortest possible time;

- The Carolina parrot is the only known historical time a representative of the parrot family of birds that lived in North America and well adapted even to winter cold weather. However, this parrot was a serious agricultural pest, actively feasting on crops and the fruits of fruit trees. This led to a large-scale hunt for the Carolina parrot, which by the beginning of the last century ended in its extermination;

- Steller's cow is marine mammal was discovered by naturalist Georg Steller, doctor of the Vitus Bering expedition, in 1741 near the Commander Islands. This animal, belonging to the order of sirens, was distinguished by its large size (up to 7 meters in length and weighing 5 tons), extremely peaceful disposition, lack of fear of people, slow speed movement and inability to dive and swim underwater. All these factors, combined with a fatal circumstance, with a very delicious meat, became the reason that Steller's cows were exterminated by sailors in just 27 years from the moment of discovery;

- Chinese river dolphin- a modern, but already classic example of the extinction of an animal species due to the development of human civilization. This is a representative of river dolphins that lived in the Chinese Yangtze River and some freshwater lakes associated with it. The Chinese river dolphin was discovered only in 1918, and in 2006 a commission of biologists stated that this type, apparently disappeared.

Extinct animals: where man is not to blame
But still, we should not forget that the disappearance of animal species is not only a consequence of human activity, but also of ordinary biological activity. This is evidenced by the abundance of animals that disappeared from the face of the Earth at a time when Homo sapiens already existed and was gradually moving towards building a civilization, but did not yet have the capabilities for the mass destruction of animals. Here are some extinct animals from BC:
- Marsupial lion is a genus of carnivores marsupials of Australia, whose representatives were largest predators continent. It was an unusually strong, powerfully muscled animal about one and a half meters long, about 70 centimeters in height and weighing from 100 to 150 kilograms. There is a rock carving of a marsupial lion found, which suggests that these animals coexisted with primitive people and disappeared no earlier than 30 thousand years ago;
- The North African (Carthaginian) elephant is one of the few animals that are an active participant in ancient history. It was these elephants that were the “soldiers” in the Carthaginian army of the great commander Hannibal, who terrified the Roman Republic during the Punic Wars of the 3rd century BC. Carthaginian elephants, which were relatively small in height, up to 3 meters, were used for military purposes before. This subspecies of elephant disappeared in the first centuries of our era, most likely due to its use in circus performances, during which wild animals fought with each other or with gladiators;


Alexander Babitsky
According to the World Conservation Union for 2008, over the past five hundred years, 844 species of animals have become completely extinct. And the saddest thing is that most often the cause of extinction of species is humans. This list shows only 10 species of animals (with photos) that became extinct relatively recently.
Thylacina, also known as the Tasmanian tiger, was the largest carnivorous marsupial known in modern times. In the wild, it is considered extinct due to constant hunting (they were a threat to sheep and other small animals) and human encroachment on their already limited habitats. Critically endangered in 1936, the last Thylacina, named Benjamin, died on 7 September at Hobart Zoo, Tasmania.
Quagga
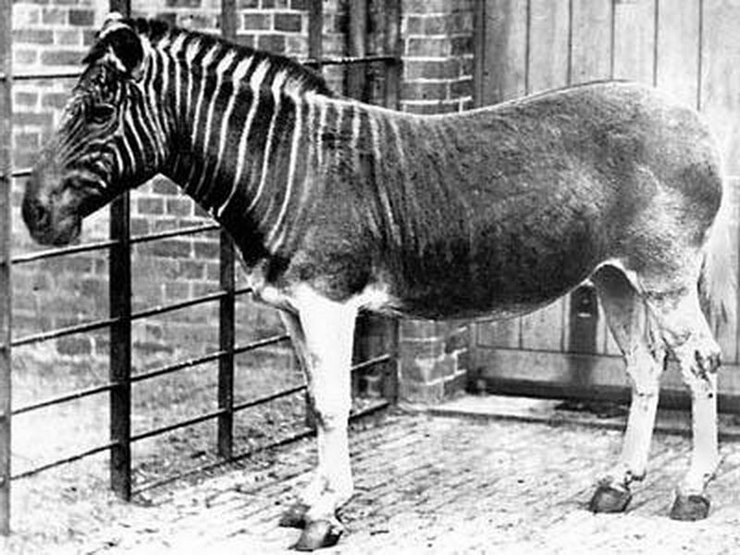

Quagga is an extinct southern subspecies of zebra. It was distinguished from other zebras mainly by stripes on the head, neck and front of the body. They became extinct due to the fault of humans because they were mercilessly hunted for their meat and skin.
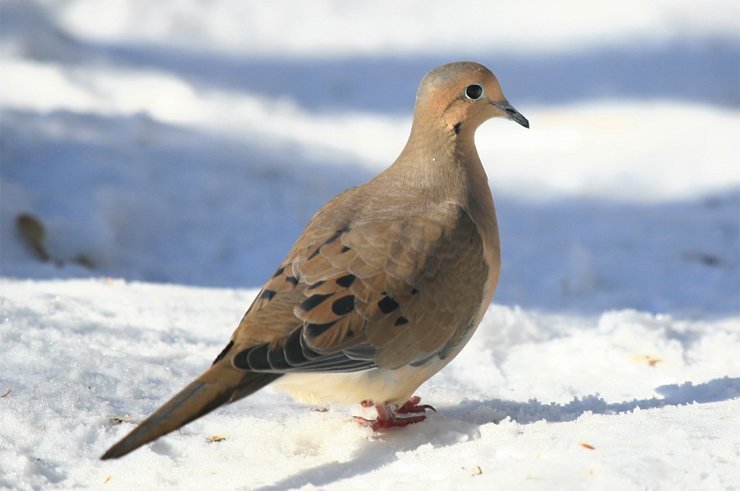

The story of the disappearance of the passenger pigeon is one of the most tragic. Until the 19th century, this bird species was considered one of the most common on Earth, total quantity which were estimated at 3–5 billion individuals. However, from 1800 to 1870, their numbers gradually began to decrease, due to the fact that the meat of this pigeon was recognized as a cheap and tasty food, especially among slaves and the poor, and also because of their multi-million-dollar flocks, which are like locusts when they see food. , rushed at her, completely destroying fruits, berries, nuts and insects. Therefore, the gluttony of the passenger pigeon irritated farmers. The last passenger pigeon, named Marfa, died alone in the zoo on September 1, 1914.
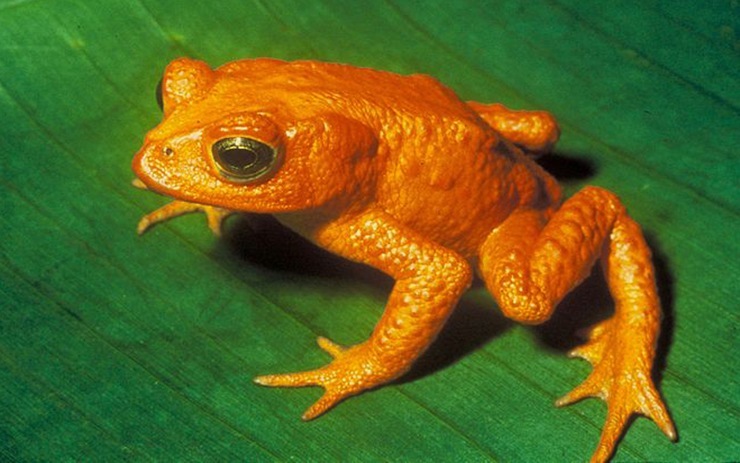

The Golden Toad was from tropical forests, which surround Monteverde, in Costa Rica. Since 1989, no one has seen a single toad of this species.
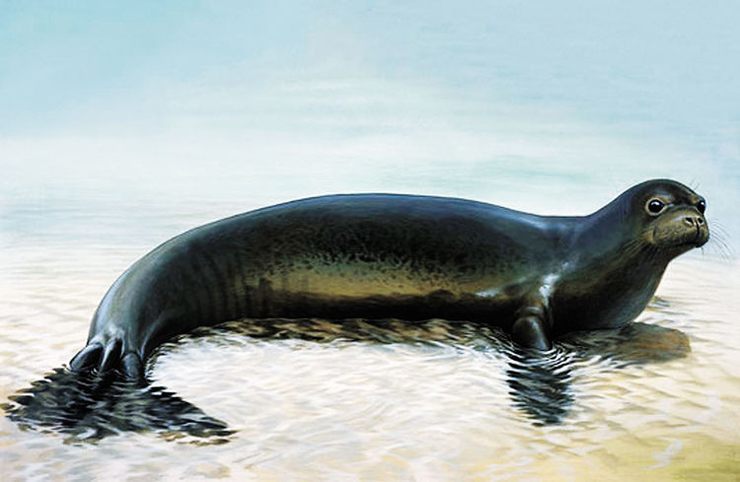

The Caribbean monk seal was the only known seal native to Caribbean Sea and the Gulf of Mexico. This species of seal was first discovered by Columbus on the coast of Santo Domingo in 1494. Officially declared extinct on June 6, 2008.

Among the recently extinct animals, the Iberian ibex has one of the most interesting stories extinction, as it was the first species to be brought back to life through cloning. But all cloned animals died seven minutes after birth. The Iberian ibex was originally from the Pyrenees (a mountain range in Andorra, in France and Spain). At the end of 1980, their number was estimated at 6–14 individuals. The last naturally born Iberian goat, who died on January 6, 2000, was named Celia.
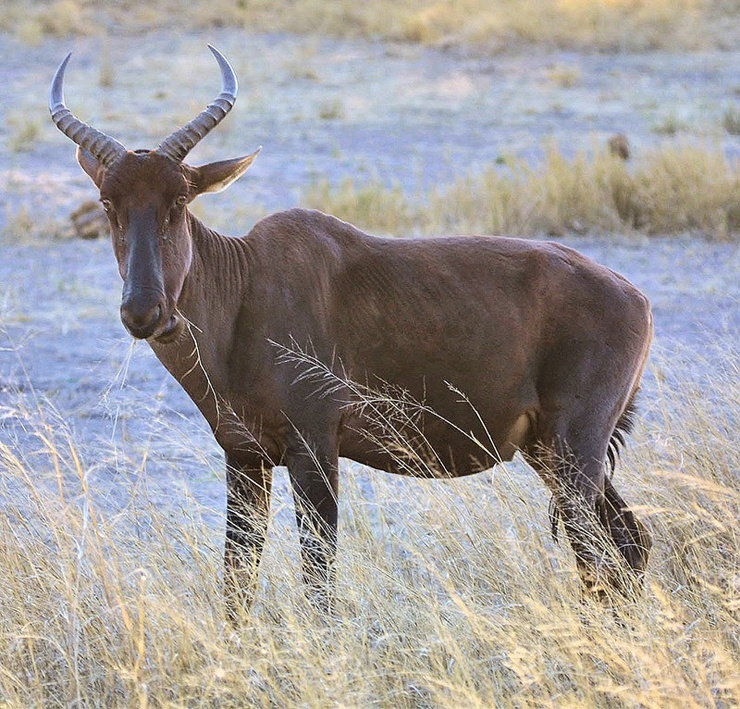

The North African antelope Bubal once roamed throughout North Africa and in the Middle East. People who live in Morocco shot these animals for fun. The last female North African antelope, the hartebeest, died in a Paris zoo in 1923.

The Javan tiger is an extinct subspecies of tigers that lived on the Indonesian island of Java. The main reason for their disappearance was the expansion of agricultural land on the island, which led to their loss natural place habitat.
 2
2
The population of our planet is increasing year by year, but the number of wild animals, on the contrary, is decreasing.
Humanity influences extinction large quantity species of animals by expanding their cities, thereby robbing the fauna of their natural habitats. A very important role is played by the fact that people are constantly cutting down forests, developing more and more land for crops, and polluting the atmosphere and water bodies with waste.
It should be noted that sometimes the expansion of megacities has a positive effect on some species of animals: rats, pigeons, crows.
On at the moment it is very important to save everything biological diversity, because it was originated by nature millions of years ago. The diversity of animals presented is not just a random accumulation, but a single coordinated working connection. The extinction of any species will cause major changes to the entire ecosystem. Each species is very important and unique for our world.
As for the endangered unique species animals and birds, then they should be treated with special care and protection. Since they are the most vulnerable and humanity can lose this species at any moment. It is the conservation of rare species of animals that becomes a primary task for each state and people in particular.
Main reasons for loss various types animals represents: degeneration of the animal habitat; uncontrolled hunting in prohibited areas; killing animals to create products; habitat pollution. All countries of the world have certain laws to protect against extermination of wild animals, regulating rational hunting and fishing; in Russia there is a law on hunting and use of wildlife.
At the moment, there is the so-called Red Book of the International Union for Conservation of Nature, established in 1948, where all rare animals and plants are listed. IN Russian Federation There is a similar Red Book, which keeps records of endangered species in our country. Thanks to the state policy, it was possible to save sables and saigas, which were on the verge of extinction, from extinction. Now it is even allowed to hunt them. The number of kulans and bison has increased.
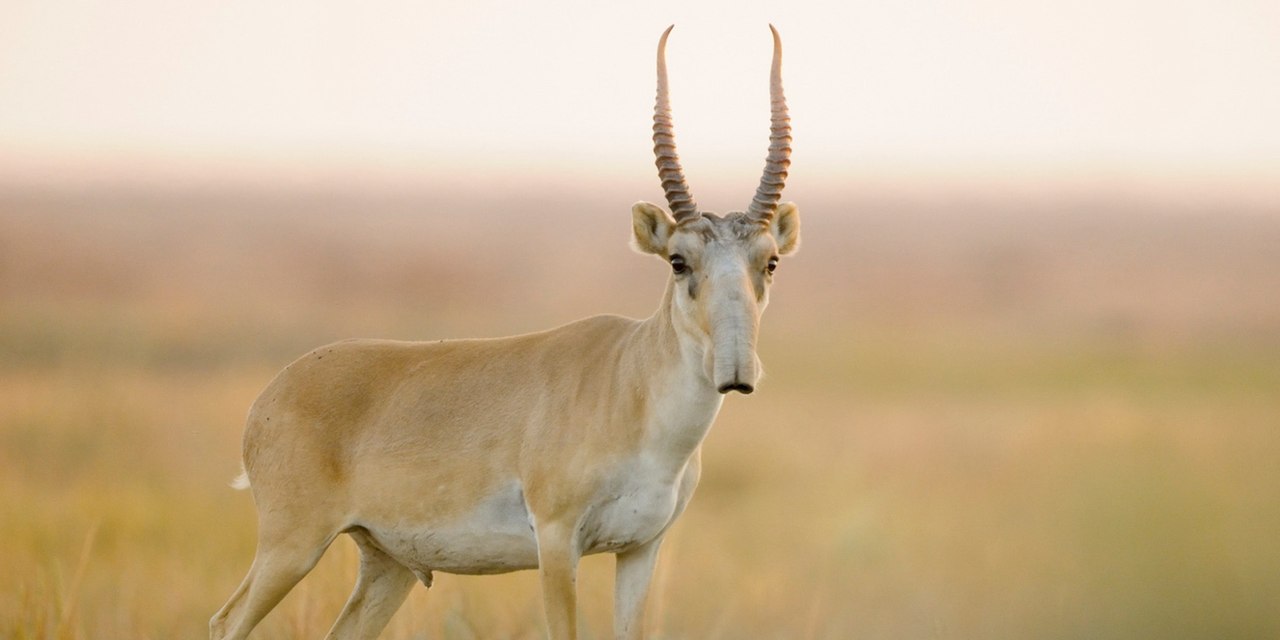 Saigas could have disappeared from the face of the Earth
Saigas could have disappeared from the face of the Earth
Extinction anxiety biological species not far-fetched. So, if we take the period from the beginning of the seventeenth century to the end of the twentieth (about three hundred years), 68 species of mammals and 130 species of birds became extinct.
According to statistics maintained by the International Union for Conservation of Nature, one species or subspecies is destroyed every year. The phenomenon of partial extinction, that is, extinction in certain countries, has become very common. So in Russia in the Caucasus, humans contributed to the fact that nine species have already become extinct. Although this happened before: according to archaeological reports, musk oxen were in Russia 200 years ago, and in Alaska they were recorded before 1900. But there are still species that we can lose in a short time.
Bison- the only remaining representative wild boars, looks like a bison. The Belovezhsky bison, larger in size and with a darker coat color, was exterminated back in 1927. There are only a few dozen Caucasian bison left.

- This large animal with orange color. There are about ten subspecies in this species, two of which are found in our country, but much less frequently.
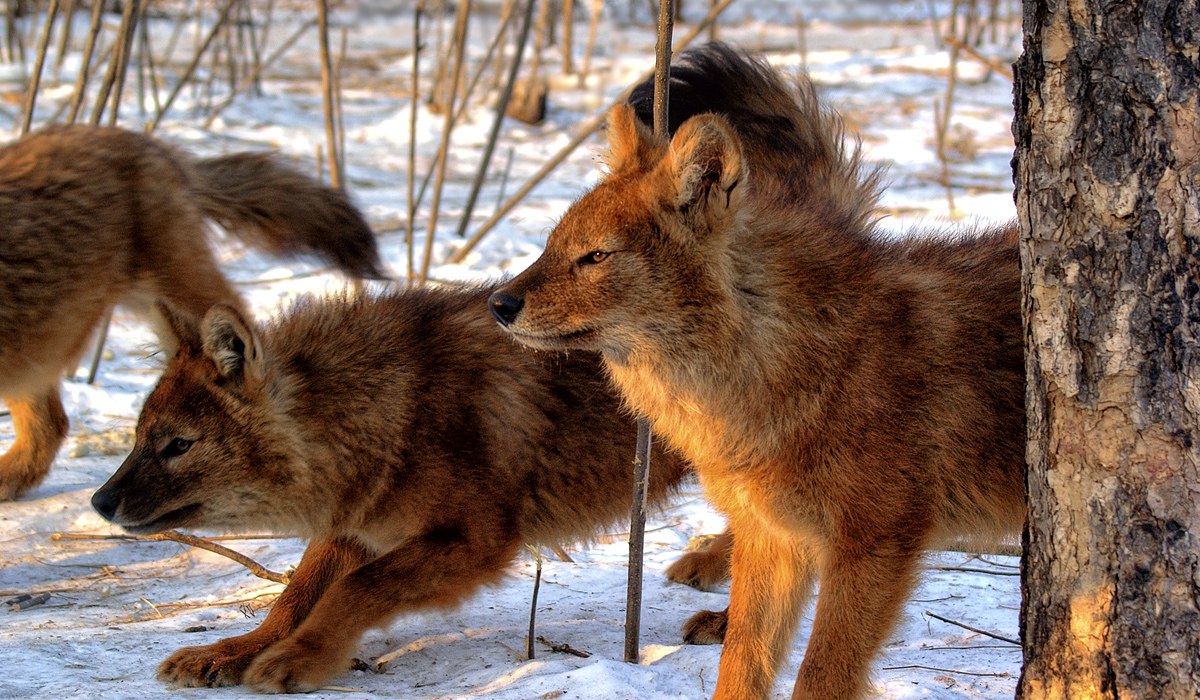

Siberian Crane- a crane that lives in northern Siberia. As a result of the reduction of wetlands, it is quickly dying out.
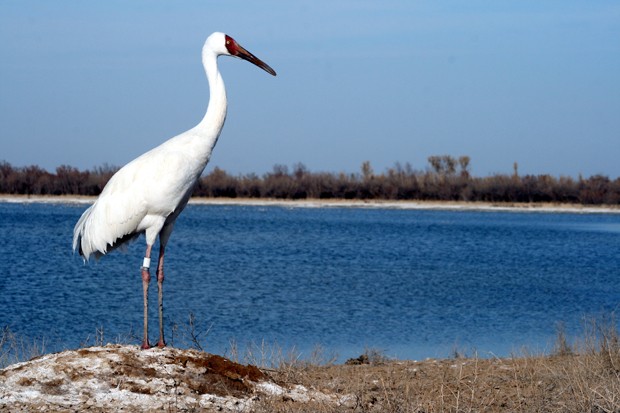

If we talk in more detail about specific species of endangered animals, birds, and insects, research centers provide various statistics and ratings. Nowadays, more than 40% of flora and fauna are in danger of extinction. Some more endangered animal species:
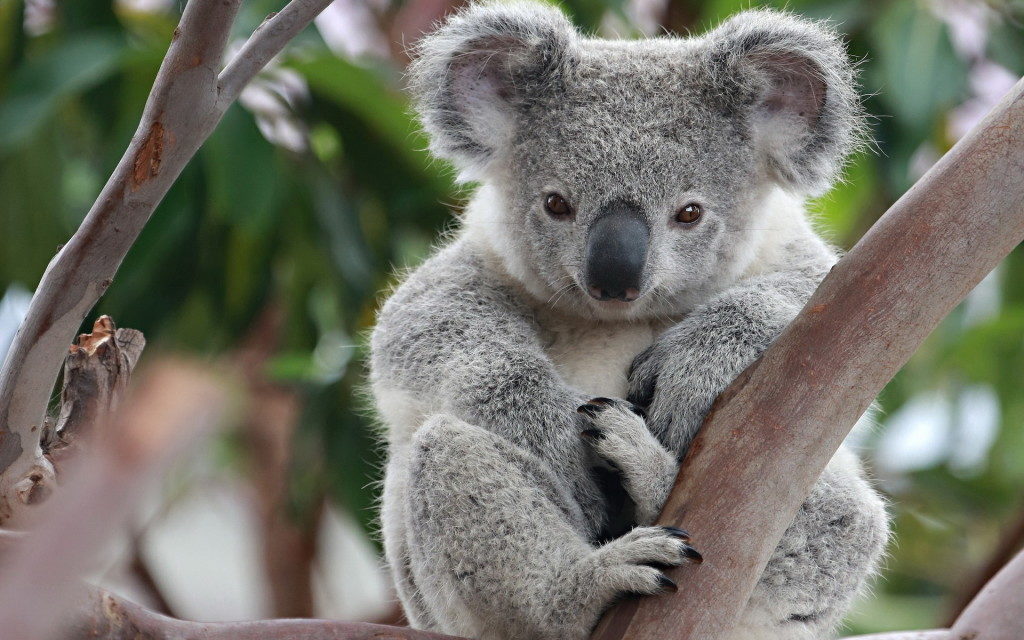
1. Koala. The decline of the species occurs due to the cutting down of eucalyptus - their food source, urbanization processes and dog attacks.

2. . The main reasons for the population decline are poaching and forest fires.

3. . Negatively affects reproduction sea lions deterioration of environmental conditions, as well as infection from wild dogs.

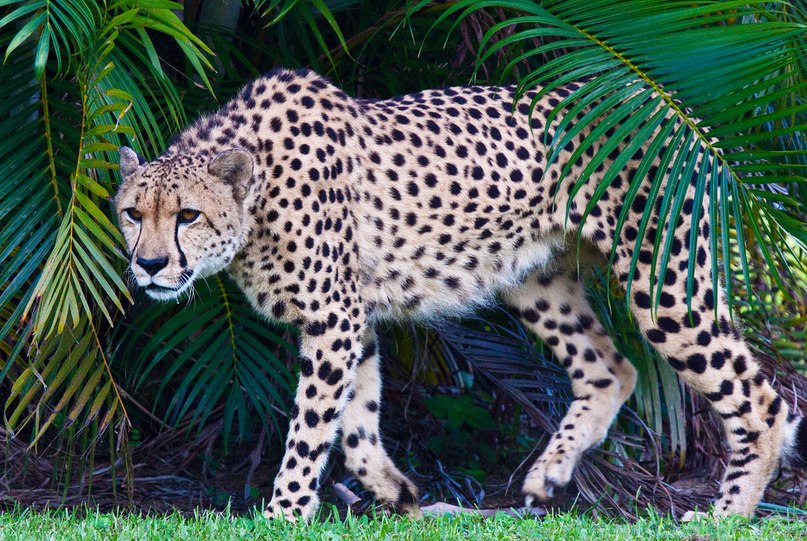
4. Cheetah. They are killed by farmers because cheetahs prey on livestock. They are also hunted by poachers for their skins.

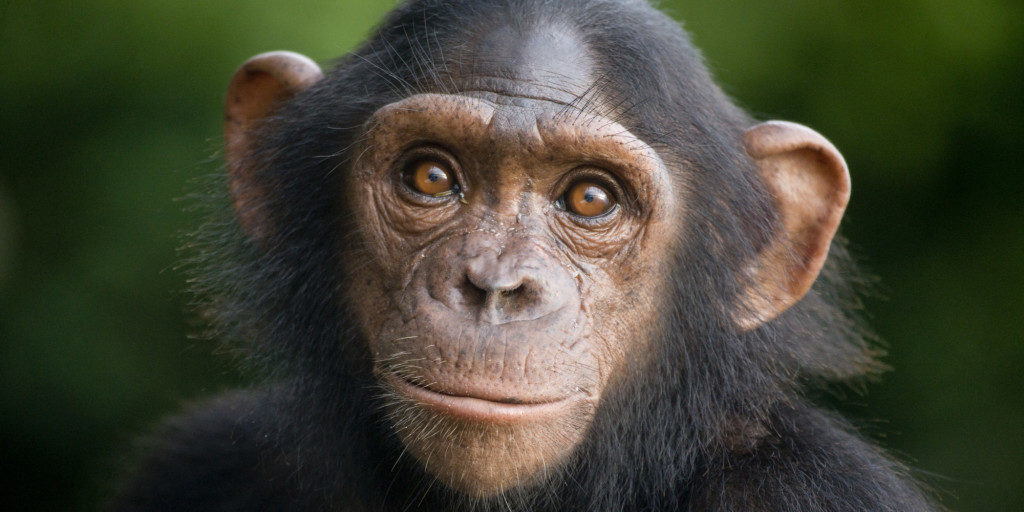
5. . The decline of the species is due to degradation of their habitat, illegal trade in their young, and infectious contamination.

6. . Their population has been reduced by the change climatic conditions and poaching.

7. Collared sloth. The population is declining due to tropical deforestation.

8. . The main threat is poachers who sell rhino horn on the black market.
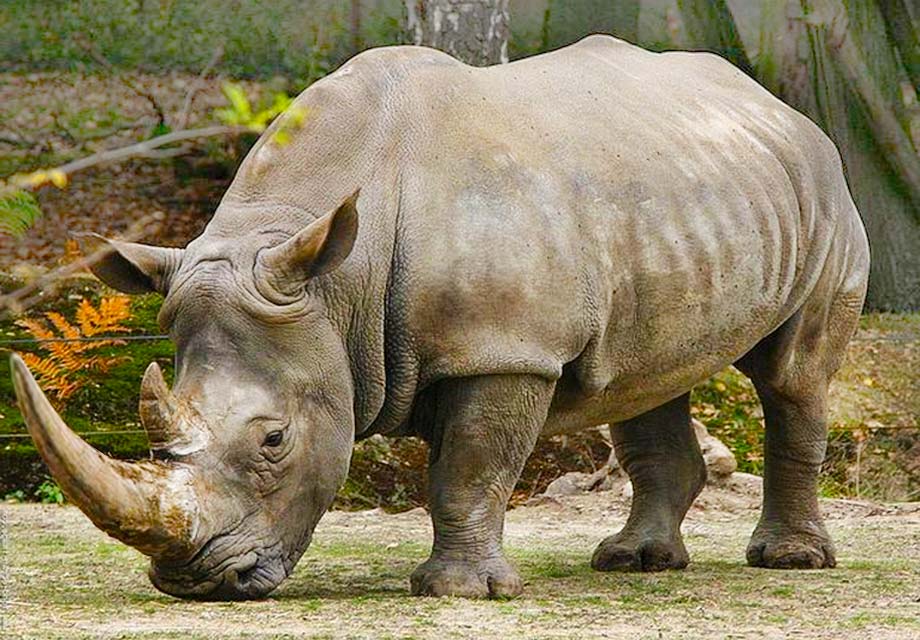

9. . The species is being forced out of its habitat. Animals have a low birth rate in principle.

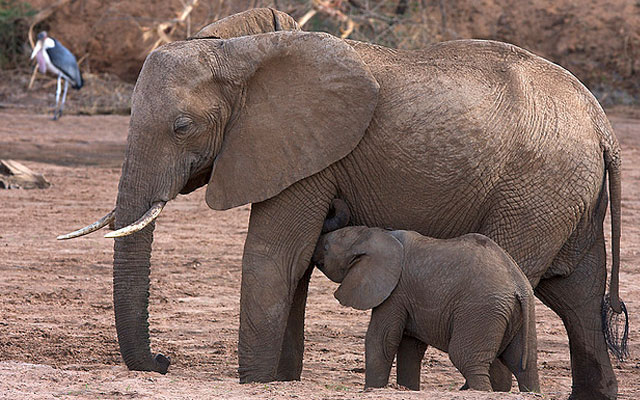
10. . This species is also a victim of poaching as ivory is of great value.

11. . This species was actively hunted for its pelts and pasture competition.

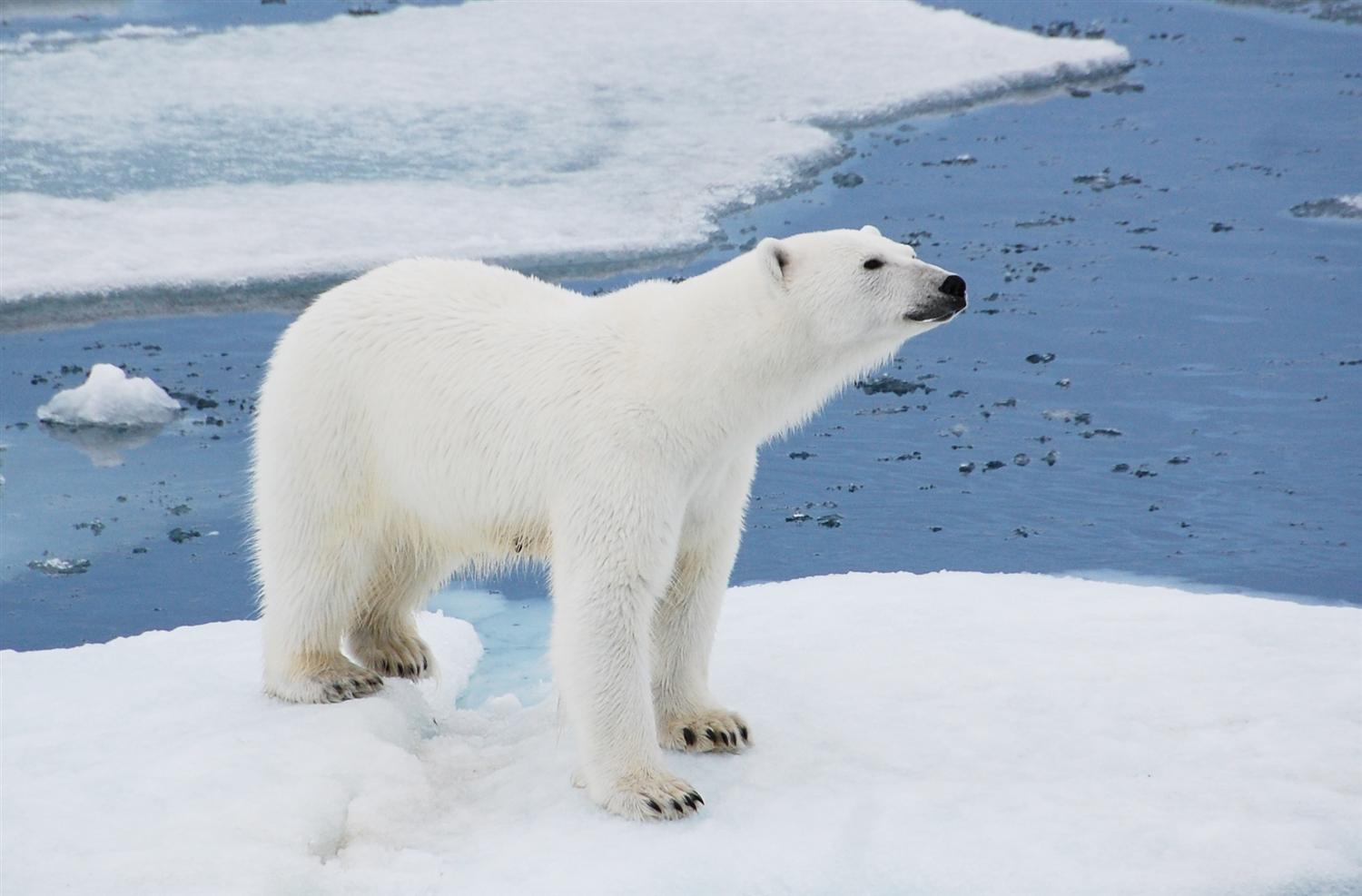
12. . Changes in bear habitat due to global warming influences the decline of the species.

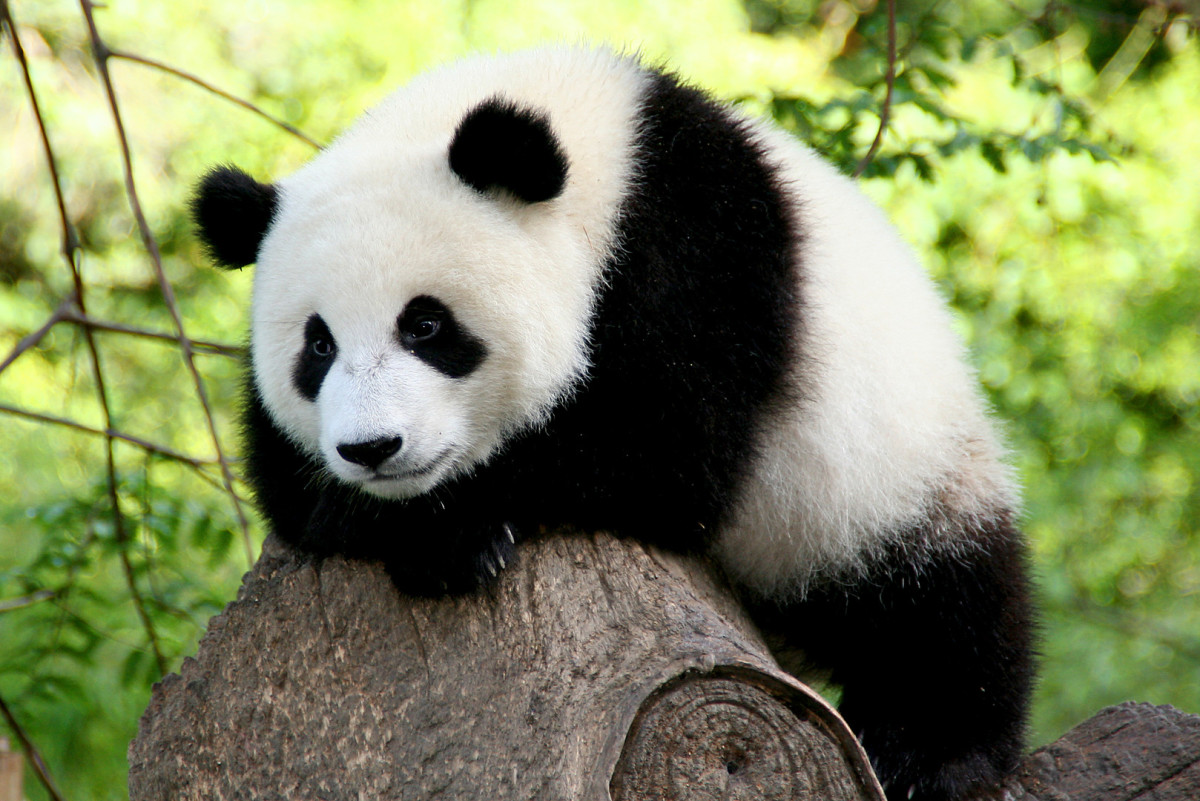
13. . The population is declining due to deforestation.

14. . The species has been reduced due to hunting and the danger of bears to humans.
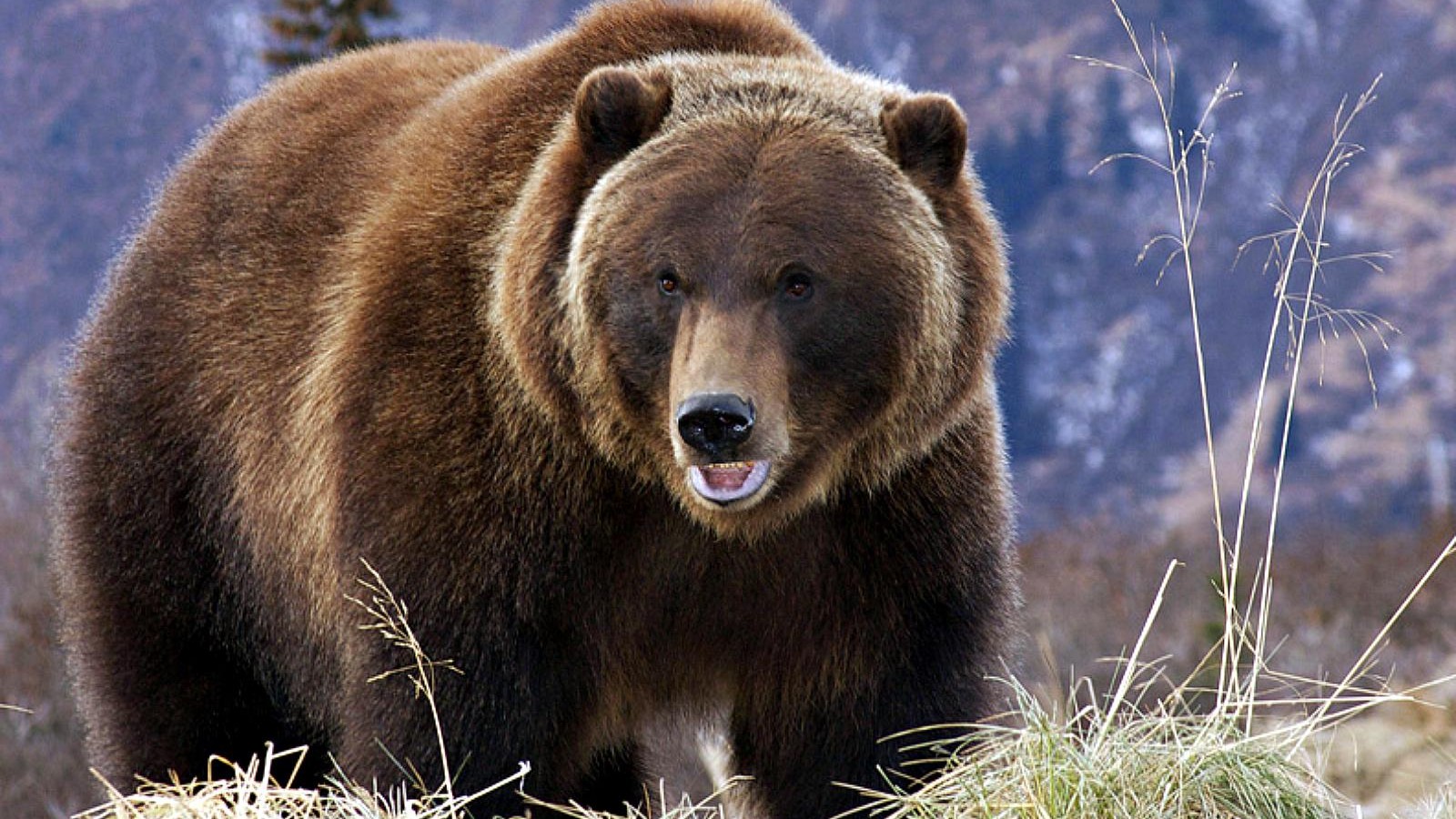

15. . The species is being destroyed due to conflicts with people, active hunting, infectious diseases and climate change.

16. Galapagos tortoise . They were actively destroyed and their habitats were changed. Animals that were brought to the Galapagos had a negative impact on their reproduction.

17. . The species is declining due to natural disasters and poaching.
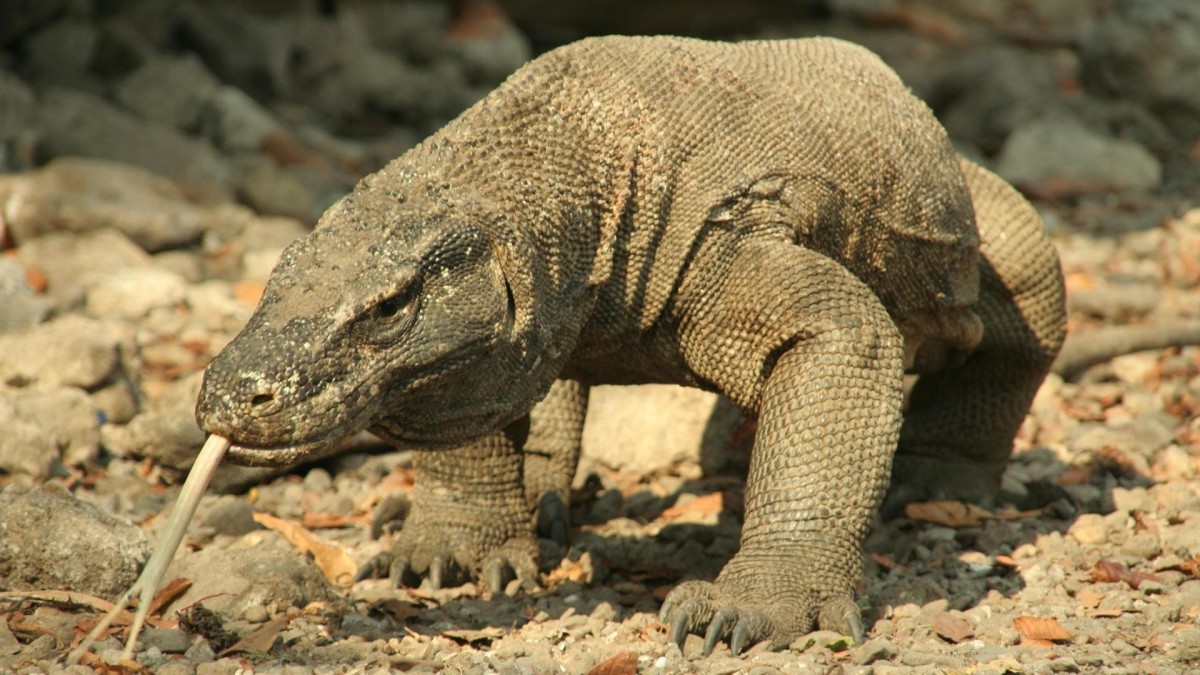

18. . The population has been reduced due to shark fishing.
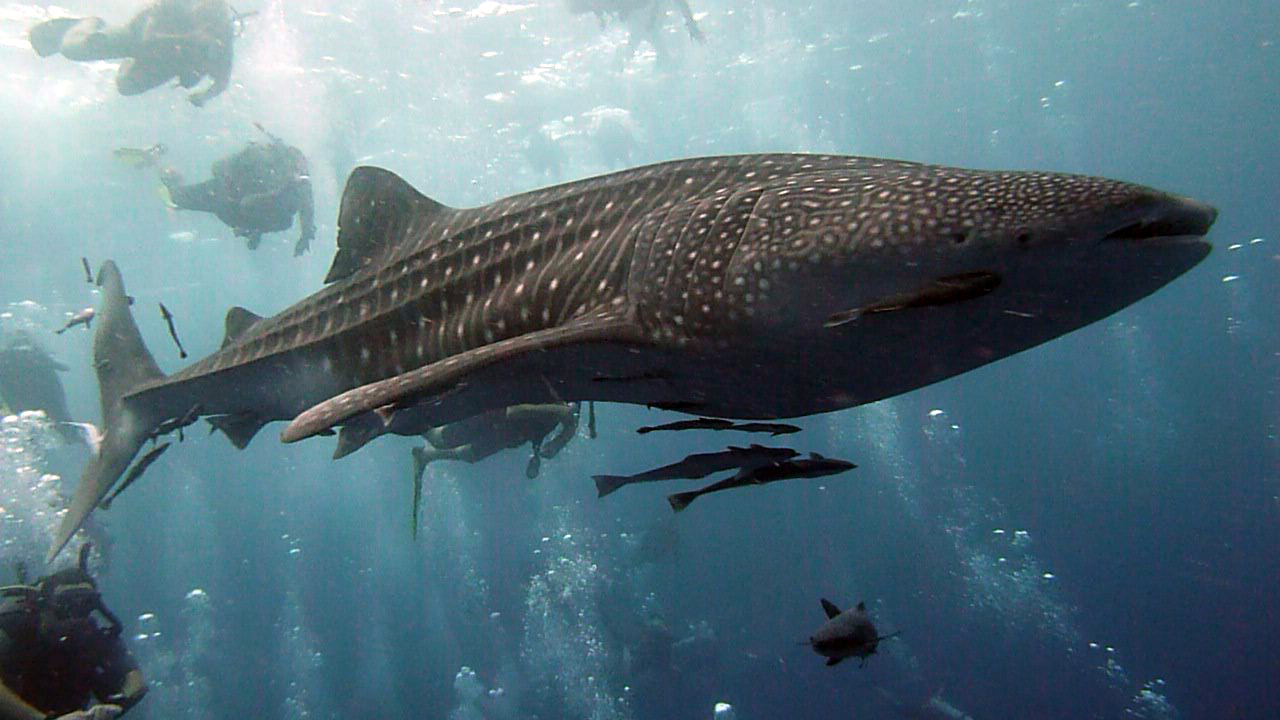

19. . The species is becoming extinct due to infectious diseases and habitat changes.

20. . Illegal trade in animal meat and bones has led to a decline in the population.
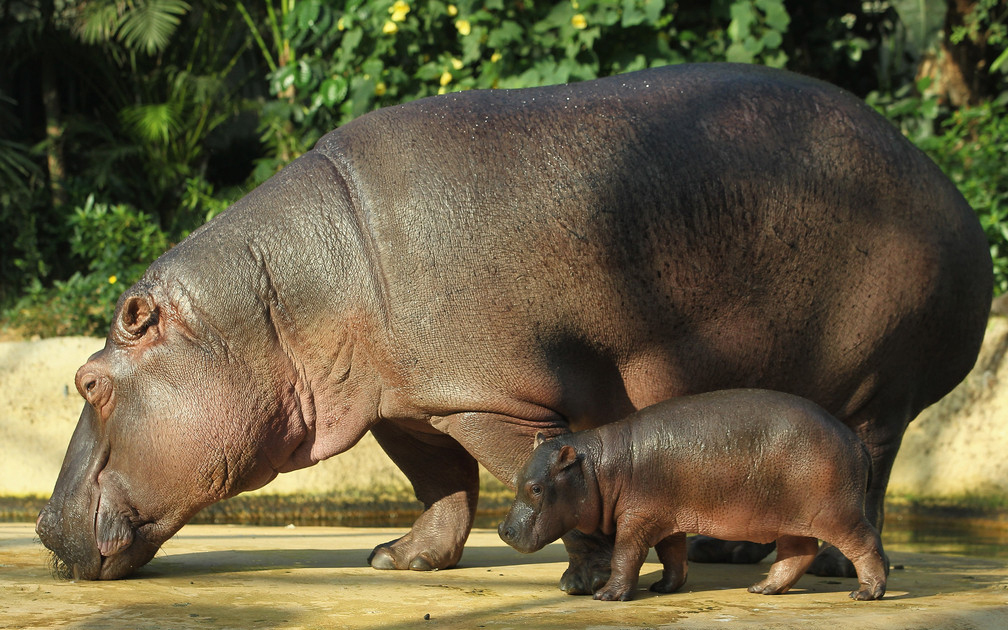

21. . The population suffers due to constant oil spills.

22. . The species is declining due to whaling.
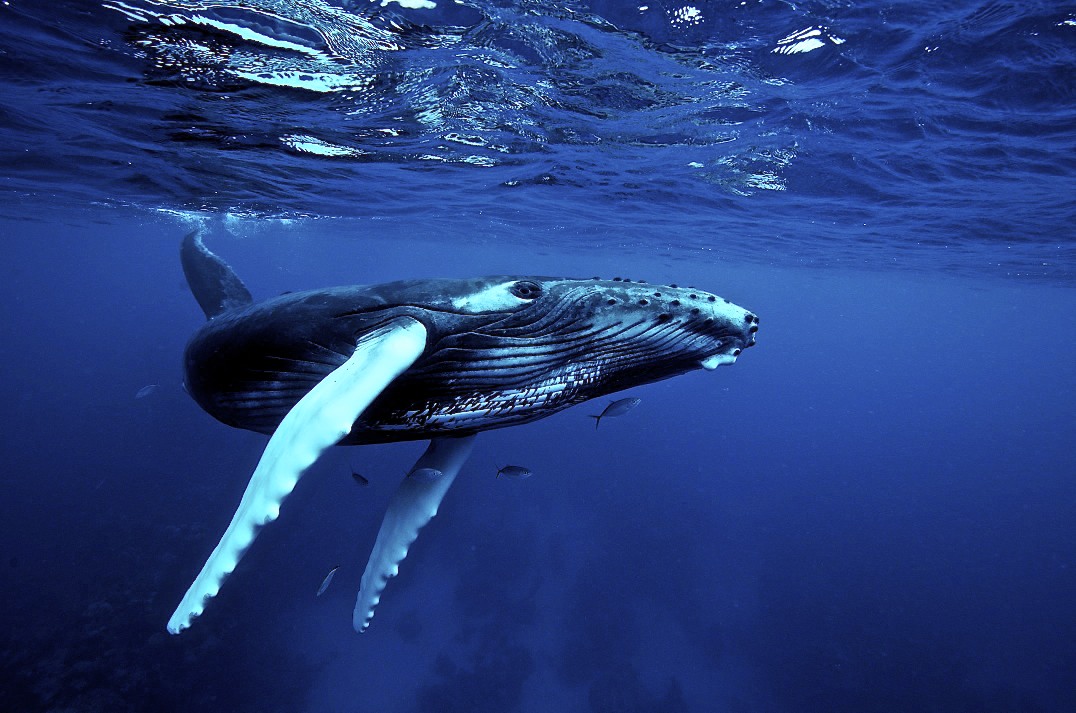

23. . The species has become a victim of poaching.
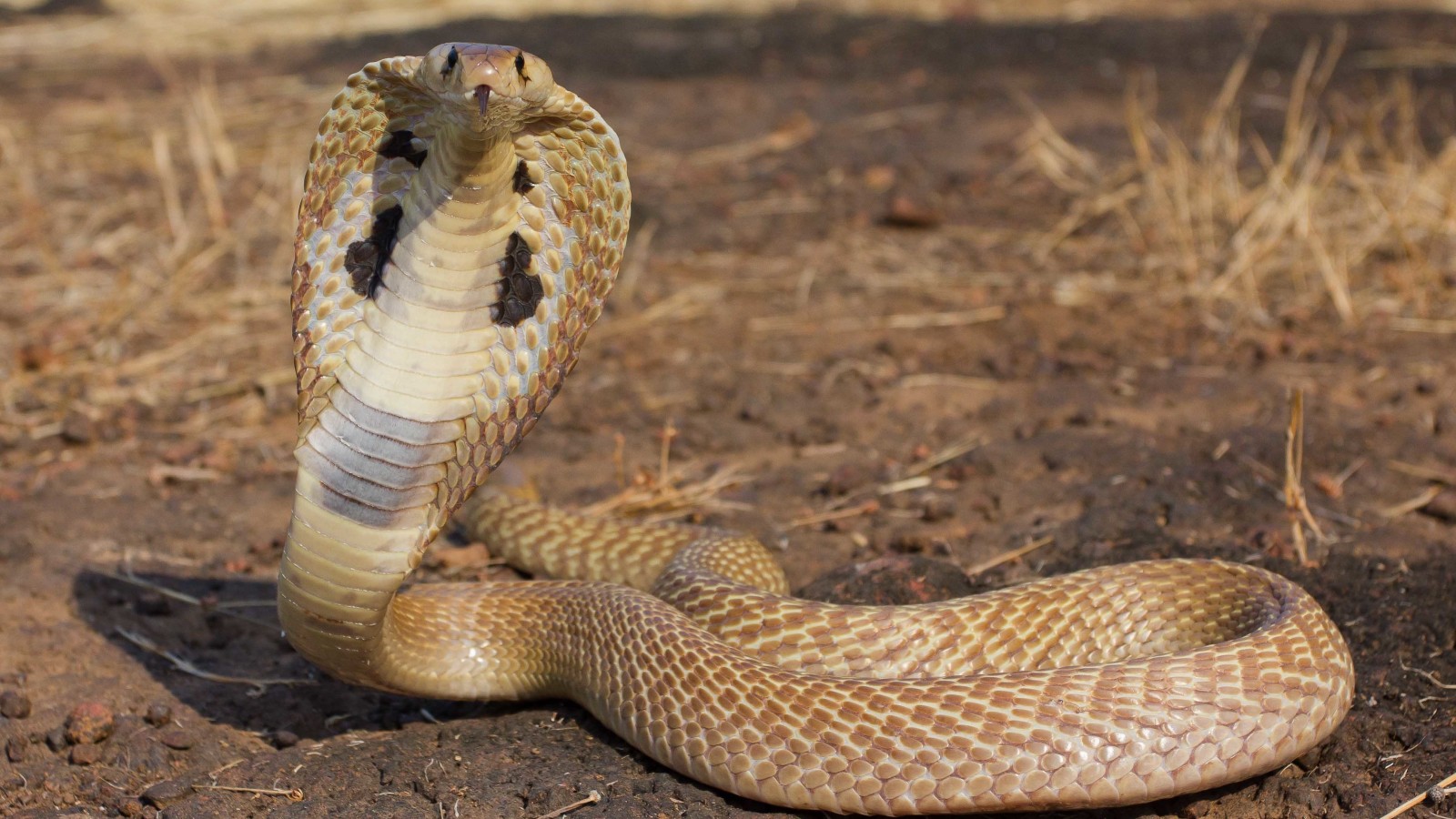

24. . Animals are suffering due to habitat loss.
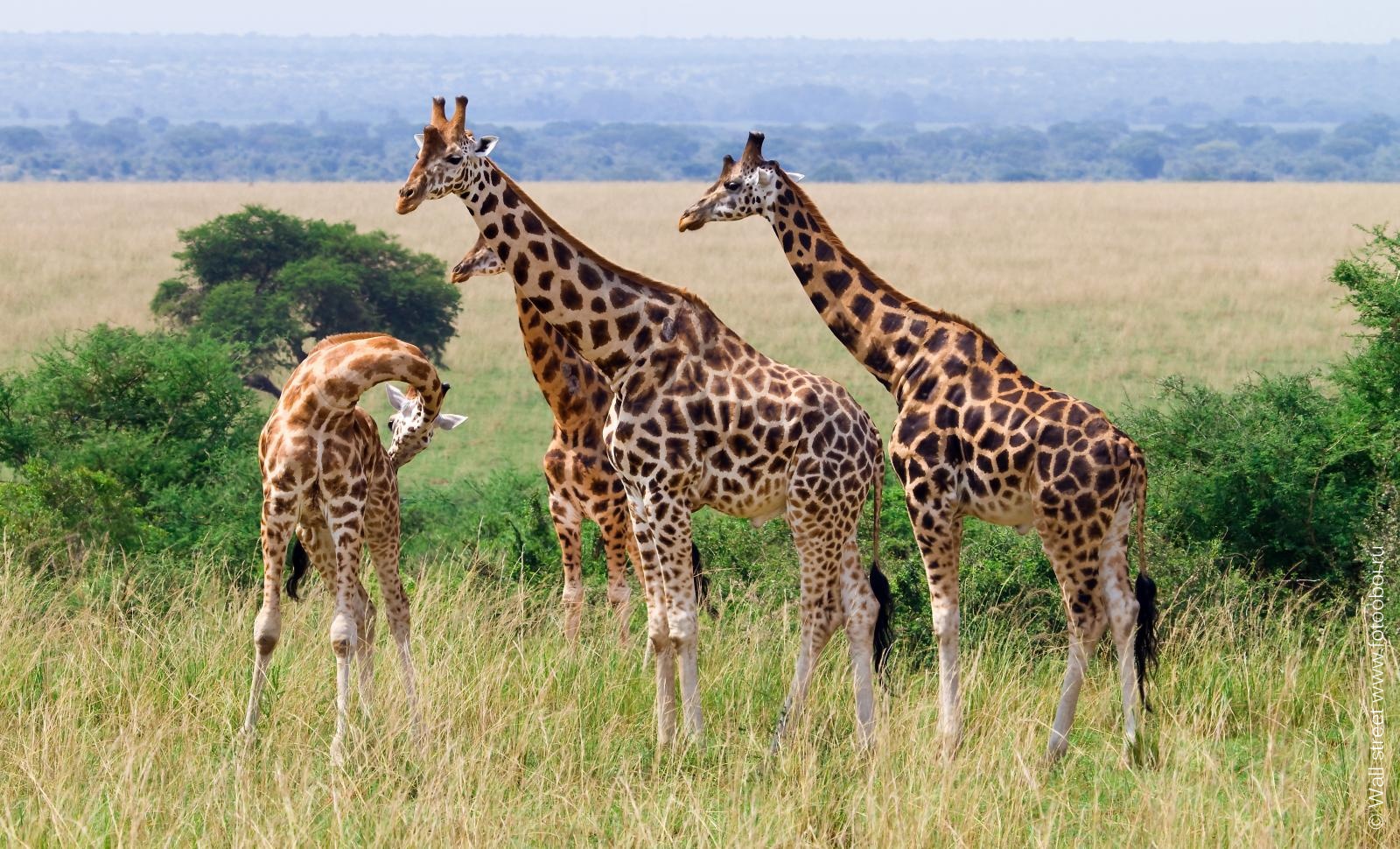

25. . The population is declining due to urbanization processes and active deforestation.
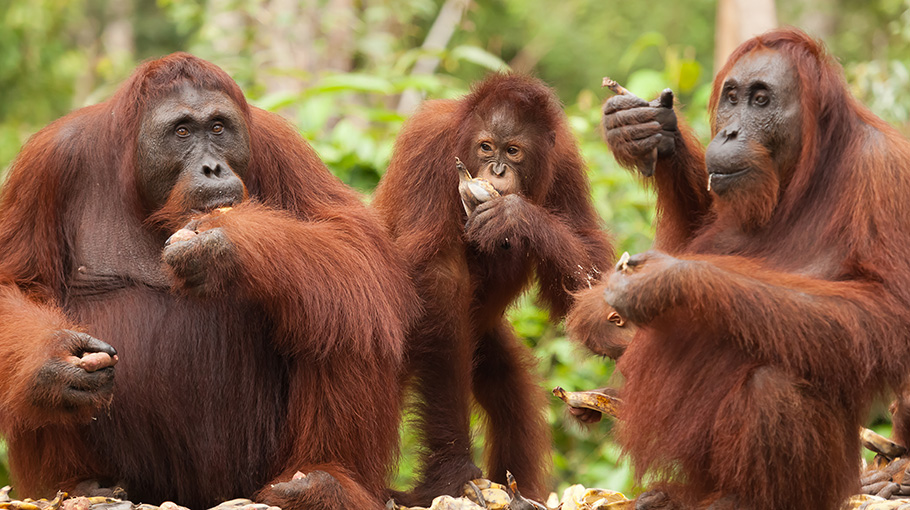

The list of endangered animals is not limited to these species. As we see, the main threat is a person and the consequences of his activities. There are government programs for the conservation of endangered animals. And every person can make a contribution to the conservation of endangered animal species.








 About the company Foreign language courses at Moscow State University
About the company Foreign language courses at Moscow State University Which city and why became the main one in Ancient Mesopotamia?
Which city and why became the main one in Ancient Mesopotamia? Why Bukhsoft Online is better than a regular accounting program!
Why Bukhsoft Online is better than a regular accounting program! Which year is a leap year and how to calculate it
Which year is a leap year and how to calculate it