Inventory accounting program for an organization. SP-TMTS (Accounting for inventory items)
The Warehouse Accounting program is designed for maintaining analytical accounting of inventory items. Analytics is carried out in the context of warehouses (materially responsible persons), accounting subaccounts (10.2, 41, 10.6, etc.) and items of inventory items. When entering information on a receipt document, warehouse cards are automatically generated in the card index. The accounting model is used based on the actual cost of a unit of inventory.
Where to start
The first thing you need to do is fill out a directory of inventory items and a directory of Warehouses (divisions, financially responsible persons). Also, to prepare the primary documents, you will need the constants of your company: TIN, KPP, name, bank details, full names of responsible persons, and so on. In the Warehouse program, of course, it is possible to fill out directories, as they say, “on the fly,” that is, when entering documents, but it is more convenient when the names are already present in the directory - this way you will save your time.
Next, you need to indicate in the program the initial balances of the inventory of inventory items broken down by accounts and warehouses (divisions of your enterprise or financially responsible persons). This can be done in the main menu item “Data”, “Entering initial balances”. You can check the correctness of the input using the “F10 Calculation” button. This function calculates the amount of initial balances at accounting prices for the specified subaccount and the selected warehouse.

In our warehouse accounting program, another method of entering initial balances is possible. For example, you have balances as of January 1 of the current year according to inventory data. In this case, in the “Receipt” section, you must enter a receipt document dated December 31 of the previous year, indicating the corresponding debit subaccount, quantity and accounting price for each item of inventory. After such a document is completed, warehouse accounting cards will be entered automatically in the inventory file.
When maintaining warehouse records, we have primary documents for the receipt of goods and materials from Suppliers, as well as documents for consumption (shipment to the buyer, internal movement between divisions of the enterprise, write-off acts). The logic of working with our warehouse program involves first entering documents for receipt, and then processing outgoing documents. The case when it is necessary to issue consumable documents without receiving inventory items is also implemented in our warehouse program, but we will consider it separately later.
Entering a receipt document from a supplier
To enter a document for the posting of inventory items, select the menu item “Data”, “Receipt”. In the window for entering documents for receipt, select the Warehouse to which the items will be posted according to the receipt document. To add an item to the document, click the “F5 Add” button and in the input card that opens, indicate the name from the directory by clicking the “Name” button, quantity, accounting price or amount with or without VAT. In the same window, indicate the number, date of the document and supplier from the “Organizations” directory. 
When you enter the next name, the document details will be copied automatically. Upon completion of entering the receipt document, check the correctness of the entry by pressing “F10 Calculation”. If transport services for delivery are highlighted as a separate line in the document, then they can be included in the cost of the item by clicking the “F12 Include amount” button. 
You can then continue entering the next document. The package of entered receipt documents will be reflected in the accounting when it is carried out. When leaving this point, answer “Yes” to the question “Post documents for receipt of goods and materials?” and the package of documents will be reflected in the accounting. After this, in the inventory card file at the selected warehouse (division), we will find warehouse accounting cards. The card index thus models a real object. You can also answer “No”, in which case the documents you entered will be saved in a temporary database. You can later select the same menu item and continue entering information. Posted documents are automatically registered in the journal of receipt documents, which can be selected in the main menu item “Documents”, “Documents for receipt of goods and materials”. 
Only at this point can you make corrections to an already posted receipt document from the Supplier.
Entering a consumable document
The consumption of inventory items is associated with real processes of production activity: internal movement of goods and materials between departments (warehouses) of your enterprise, drawing up an act for writing off inventory items consumed in the production process, releasing materials to the outside on tolling terms, moving goods to a retail outlet , shipment of goods or finished products to the buyer. In our warehouse program, this is implemented by various journals of consumable documents: “Invoices (outsourcing)”, “Internal movement” journal, “Write-off acts” journal, “Retail supply”. Depending on the operation, select the appropriate expense journal.
Internal movement
For example, we need to transfer several items of inventory items to production. The primary document in this case will be the invoice for internal movement. Select the magazine “Internal Displacement”. By clicking the “F5 Add” button, we create a new document, then click the “F4 Open invoice” button and the “Ins Add” button. 
The addition occurs based on data about the balances in the card index. In the window that opens, enter the number of moving inventory items and press the “F10 Select” button and when asked: “Which Warehouse”, indicate the department where the inventory items will be capitalized. Items with a quantity greater than zero will be added to our document. Next, click the “Exit” button and answer the question “Move the invoice?” We will answer “Yes”. The specified items will be written off from the division where they were recorded and will be capitalized in the division that we indicated in response to the question: “Which warehouse.” Thus, the card index will model the consumption and receipt for the specified items based on our invoice for internal movement. In the list of invoices for internal movement, you can create a printed form of primary documents: invoice for internal movement, requirement-invoice of the standard form M-11, invoice for the release of materials to the third party on tolling terms of the standard unified form M-15. When creating printed forms, indicate the requested fields. 
Write-off acts
To reflect the write-off operation of inventory items used in the process of production activities, as well as the write-off operations for inventories that have become unusable during operation, select this document journal. To add a new document, press the “F5 add” button, then “F4 open invoice”. We will use the “Ins add” button to add a list of items to the document based on warehouse accounting data on item balances modeled in the inventory card file. In the window that opens, enter the amount of inventory items to be written off and click the “F10 Select” button, and when asked for additional information for write-off, indicate the cost account according to the chart of accounts and click the “Next” button. 
Items where a quantity greater than zero was indicated will be added to our document. Next, click the “Exit” button and answer the question “Post the document?” We will answer “Yes”. The indicated names will be written off from the department where they were recorded. In the journal of documents for write-off, you can generate a printed form of primary documents for write-off of inventory items: an act for the write-off of inventories due to unusability, an act for the write-off of inventories in the process of production activities.
Invoices. Vacation on the side
Documents for the Buyer are completed in this journal of consumable documents. This journal also serves to enter documents for the implementation of works and services.
If the buyer has been issued an invoice for payment, you can proceed as follows: in the “Invoices for payment” journal, find the invoice issued to the Buyer and press the button “F11 transfer invoice to s/f” and answer “Yes” to the question “Transfer invoice No.” . As a result of our actions, a new document will be generated in the “Invoices” journal. External leave”, and the contents of the invoice for payment will be copied to this added document automatically. With this method, to obtain a printed form of shipping documents, we need to select a document in the journal and press the “F9 print” button. In the window for selecting printed forms, we will indicate the document we need and fill in additional information for the selected document in a new window. 
Now let's consider the case when the payment invoice was not generated for the Buyer. In the magazine “Invoices. Outsourcing”, press the “F5 add” button and indicate the Buyer from the “Organizations” directory, document type: for goods and materials or services, document currency. The "Save" button will add a new document to the journal. 
To fill in the contents of the document, press the “F4 Contents” button and then the “Ins Add List” button to add several items from inventory balances or the “F5 Add” button to add one item from the inventory directory. When using the “Ins Add List” function, we indicate the number of goods to be shipped. The “F10 selection” button will add an item to our document, where we indicated a quantity greater than zero. Selling prices for items selected in this way will be taken from the inventory directory. In this case, the calculation of selling prices for the shipment of goods can also be carried out using the “F9 set % markup” button. We indicate the markup percentage, and the selling price of the product will be calculated by the program. In our product accounting program, it is also possible to use the functionality of selling price groups when using an electronic price tag. Let’s assume in our example that our company is still delivering the shipped goods to the Buyer’s warehouse. To add a line about transport services provided to a document in the document journal “Invoices. External leave”, press the “F1 Services” button and in the window that opens, enter the name of the services and their cost. To generate printed forms of shipping documents, press “F9 print”, specify the document form and additional information on the selected form. Our program implements the generation of the following forms of primary documents for sales: invoice, consignment note in form TORG-12, standard work acceptance certificate, certificate of cost of work performed in form KS-3, acceptance certificate for services rendered and recommended Federal Tax Service of Russia forms of a universal transfer document. It should be noted that it is possible to connect custom document forms for registered users of the Warehouse Accounting program.
Let us now consider the purpose of other menu items in the Warehouse Accounting program in more detail.
1. Directories
1.1. Materials, goods– a directory of inventory items, which serves to speed up the entry of incoming documents. The directory contains information about the name of the goods and materials, its specification (for example, article number or other additional characteristics), unit of measurement, country of origin, customs declaration number, and what taxes this type of goods and materials is subject to. You can also additionally indicate the purchase price and selling price for goods, membership in the specified group of goods, and for packaged goods - packaging: units in containers, registration and selling prices per unit. Additional information serves to facilitate the preparation of consumable documents. The directory implements a quick search by name using the first characters and a search by the occurrence of a phrase in a name or specification.
1.2. Warehouses (divisions)– a directory of warehouses, departments, materially responsible persons at the enterprise.
1.3. Organizations– a general directory of third-party legal entities and individuals of the intangible asset program. Contains information about third-party organizations and individuals. Suppliers and buyers of inventory items must be entered in the directory.
1.4. Enterprise employees– general directory of the NMA program. For the Warehouse Accounting program, it is auxiliary and is used to indicate the storekeeper, the person responsible for controlling the release of goods and materials, etc.
1.5. Chart of accounts– a general directory of the intangible assets program, containing accounts and sub-accounts of accounting.
1.6. Objects of analytical accounting– auxiliary reference book, optional for use. It is intended for maintaining additional analytical records of the program user.
1.7. Inventory price groups– a directory of product price groups, used when selling goods, when the selling price depends on the category of the buyer.
2. Data
2.1. Inventory card file– the program menu item is intended for viewing warehouse accounting cards, receipts and expenses for the selected card. 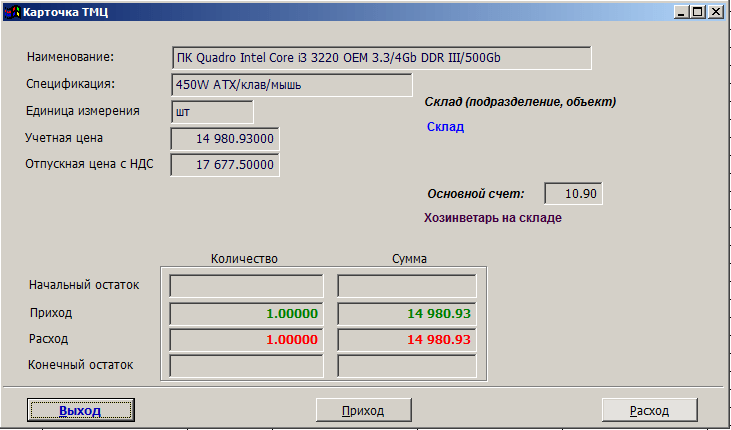
2.2. Coming- the item is used to enter primary documents about the receipt of goods and materials (waybill, invoice). If the invoice and invoice numbers are different, it is recommended to use the invoice number when entering. Entering a document begins by indicating the Warehouse (division, materially responsible person), then the program will allow you to add names. By clicking the “F5 Add” button, a window for entering a card for the name of the receipt document will appear. Specify the name of the inventory items from the directory by clicking the “Name” button. Find the required name in the directory and press the “Enter Select” button. Next, you need to indicate the quantity of receipt, the accounting price, if it differs from the specified price in the inventory directory, as well as the date, receipt document number, posting and select the supplier (counterparty) from the directory of organizations. Confirm your information by clicking the “Save” button. When entering a receipt of the following name for a document, the fields: Date, Document number, debit, Credit, Supplier will be copied and will not require entry. Having completed entering the receipt document, you can check the correctness of the entry by pressing the “F10 Calculation” button. This function allows you to calculate the amount for a receipt document. In the case of a general taxation system, the following will be calculated: amount excluding VAT, amount of VAT, amount including VAT. A very useful function “F12 Enable amount” is also available in this menu item. It allows you to include other expenses, such as delivery services, in the cost of a unit of inventory items. Thus, the actual cost of a unit of goods and materials is formed, which is as close as possible to the real cost of the unit.
2.3. Entering initial balances– the menu item is used to enter the initial balances of inventory items in the context of Warehouses (divisions, financially responsible persons) and accounting subaccounts.
2.4. Inventory card– a program menu item intended for viewing, by the specified name of inventory items, balances in Warehouses, warehouse accounting cards with accounting prices, documents for receipt and expense for this name of inventory items.
2.5. Closing the period– a service point necessary for transferring data on the receipt and consumption of inventory items to the archive. In this case, the size of the working database is significantly reduced and the performance of the program increases. The item is available only to program users who have Administrator priority with a value of 99, indicated from the main window of the NMA program in the “Settings”, “Users” item.
2.6. Restoring a closed period– a service menu item designed to restore data from an archive.
3. Documents
3.1. Invoices for payment– the item is used to issue invoices for payment of goods, works, and services. The sequence of user actions is as follows: press the “F5 add invoice” button, then the invoice card window for payment will open. 
In the window that opens, specify the buyer from the directory by clicking the “organization” button, the fields date and account number are generated automatically (if necessary, they can be changed), account type, account currency, then confirm the creation of a new account by clicking the “Save” button. If you are preparing an invoice for services or work provided, you can use the “F1 Services” button. In the window that opens, specify the name of the work (service), unit of measurement (for example, “month,” “hour”), price including VAT or price without VAT and click the “Add” button. 
You can specify an arbitrary number of lines in the invoice for the services provided. The contents of the account can be viewed by pressing the “F4 Contents” button.
To issue an invoice for payment for goods, when adding, you must specify the “Invoice Type” with the value “On Inventory and Materials,” then click the “F4 Content” button. Using the “Ins Add several items” button, you can specify the quantity by item from the card index. The “Actual quantity” column shows the availability of inventory items in the warehouse from the “Warehouse” column. Having completed entering the quantity, press the “F10 Select” button, then items of inventory with the specified quantity greater than zero will be moved to the contents of your account. If selling prices were indicated in the inventory book, then they will also be indicated in the document. After completing the input, press the “Exit” button or the Esc key and you will return to the window with a list of issued invoices for payment. By clicking the “F9 Print” button, you can generate an invoice for payment in MS Excel and print it. 
The menu item of the Warehouse Accounting program “Invoice for payment” contains other useful functions for the work of an accountant: for example, transferring a selected invoice for payment to the journal of issued invoices, viewing a reconciliation report with the buyer, and there is also a function for copying an already issued invoice.
3.2. Invoices. Vacation on the side– the program menu item is used to prepare primary sales documents: invoices, invoices, delivery notes in the TORG-12 form, acceptance certificates for work performed (services rendered), certificates of the cost of work performed in the KS-3 form. If an invoice was issued for payment to the buyer, then it can be transferred to the invoice journal. How to do this is described in paragraph 3.1. If it is necessary to issue a new invoice, then the sequence of user actions is similar to issuing an invoice for payment: click the “F5 Add” button, then the invoice card window will open. In the window that opens, specify the buyer from the directory by clicking the “organization” button, the fields date and invoice number are generated automatically (they can be changed if necessary), account type, account currency, then confirm the creation of a new document by clicking the “Save” button. In the intangible property program, it is accepted that the invoice number coincides with the number of the act or invoice. This assumption makes it easier to search for paper documents if necessary and complies with the requirements of Russian legislation when maintaining accounting records. If you are drawing up a document for services or work provided, you can use the “F1 Services” button. In the window that opens, specify the name of the work (service), unit of measurement (for example, “month,” “hour”), price including VAT or price without VAT and click the “Add” button. You can specify an arbitrary number of lines in the document for services provided (work performed). The contents of the invoice (act, delivery note) can be viewed by pressing the “F4 Content” button.
To prepare documents for the shipment of goods, when adding, you must specify the “Invoice Type” with the value “On Inventory”, then, being on the added document, press the “F4 Content” button. Using the “Ins Add several items” button, you can specify the quantity by item from the card index. The “Actual quantity” column shows the availability of inventory items in the warehouse from the “Warehouse” column. Having completed entering the quantity, press the “F10 Select” button, then the names of inventory items with the specified quantity greater than zero will be moved to the contents of your document. If selling prices were indicated in the inventory book, then they will also be indicated. After completing the input, press the “Exit” button or the Esc key and you will return to the window with a list of issued invoices. By clicking the “F9 Print” button, you can generate primary sales documents in MS Excel and print them: invoice, invoice, delivery note in the TORG-12 form, acceptance certificate for work performed (services rendered), certificate of cost of work performed according to the KS-3 form.
3.3. Documents for receipt of goods and materials– this program menu item is necessary for viewing the log of documents for the receipt of goods and materials and adjusting them if necessary. When entering documents in the “Receipt” item, a receipt journal is generated automatically.
3.4. Internal movement– menu item of the Warehouse Accounting program, necessary for modeling the internal movement of inventory items from warehouse to warehouse, from account to account. The sequence of user actions is almost the same as when preparing documents for external leave: press the “F5 Add” button and a line corresponding to the new invoice will appear in the list, then press the “F4 open invoice” button and “Add Ins”. Specify the quantity of inventory items to be moved by item and press the “F10 Select” button to confirm your actions. If necessary, you can adjust the debit of the account in the generated document, since the program will determine the credit automatically. Next, click the “Exit” button and you will return to the list of invoices. To the program’s question “Move the invoice?” You can answer "Yes". On the form with a list of invoices, the “F9 Print” button allows you to generate the following documents in MS Excel: invoice for internal movement, demand invoice, write-off act (transfer to operation).
3.5. Acts and invoices for write-off– the program menu item is used to prepare documents for writing off inventory items. The sequence of user actions is similar to the preparation of documents for internal movement.
3.6. Invoicing by due date- using this menu item is advisable when registering subscription agreements with clients in the task “Accounting and registration of agreements” indicating the invoice period for the agreement.
4. Output forms are standard reports from the Warehouse Accounting automation program.
4.1. Balances per number by Warehouses and accounts
4.2. Turnover sheet
4.3. Material reports
4.4. Inventory list
4.5. Non-standard reports
4.6. Price list
4.7. Report on a group of buyers (Sales report)
4.8. Register of issued invoices and invoices
5. Service
5.1. Packaging and reindexing are optional service functions.
5.2. The details of your own organization are the constants of your enterprise.
5.3. Warehouse program settings - in this item you can specify program constants that will be used as default data when entering documents and will greatly facilitate it. 
A particularly popular function in the settings is changing the length of the “Name” and “Specification” fields. By default, the warehouse program uses length values for “Name” of 50 characters, and “Specification” of 25 characters. You can adjust the length of the specified fields by clicking the “Setting the length of the Name and Specification fields” button. If your organization is engaged in the provision of services, then it may be useful to make the length of the field in the “Sales” table longer than in other tables.
Conclusion
The Warehouse Accounting program allows you to simulate the movement of inventory items when using the accounting method based on the actual cost of a unit in real time, therefore, the program pays much attention to the convenience of document entry. This allows you to significantly reduce their preparation time and thus increase staff productivity. It is recommended to adhere to a logical sequence when entering documents: first of all, documents for the receipt of goods and materials should be entered, and then for internal movement or consumption.
Copyright © 2019, site
All rights reserved. Copying of materials is permitted only with written permission from the administration.
On this page you can download the free warehouse program “Info-Enterprise”. It differs from the paid versions in that it has somewhat limited functionality, but is quite suitable for beginning entrepreneurs who are not yet ready to purchase a program for product accounting. See what functions are disabled in it below.
The advantage of using free product accounting programs The fact is that you don’t have to look for it, order it, or purchase it. You just need to download it from the site. It is easy to install and easy to learn. It won't work - use educational videos! They are installed along with the program.
Attention!
This is not a demo version, it is a full-fledged working product accounting program, but it is free. It does not contain any restrictions on work, including restrictions on time, date, number of documents, volume of turnover, printing of documents, etc. Its capabilities are consistent with the documentation (except for the functions listed below).If you currently keep track of goods in other programs, then you do not need to enter everything again. You can transfer reference books from Excel. In addition, if you have installed commodity accounting programs such as “1C: Trade and Warehouse” or “1C: Trade Management”, then you will be able to transfer not only directories, but also most of the entered documents.
|
|
|
Why is it free? What's the catch?
Due to the great competition in the software market, more and more companies are forced to release free products in order to somehow lure potential buyers to their side. And our free warehouse accounting program is no exception to this. Our main calculation is based on the fact that you will like our product, you will get used to it and at some point you will want some kind of greater service, greater opportunities. And then we will offer our paid products.What features are disabled in the free version?
The program has all the functions for product accounting! Only those that are not needed by small or start-up companies are disabled:- Possibility of simultaneous work by several users with a common database over the network.
- Differentiation of user access rights to different data and areas of work.
- Database administration tools: optimization tools, logging user actions, etc.
- You cannot program in a built-in language, modify existing ones or develop your own forms, reports, or change operating principles.
- The free product accounting program cannot be integrated with our other products for comprehensive enterprise automation.
You can compare the capabilities of the free program and paid versions in more detail at. If you still need any of the listed functions in your work, write to us by email. If you are not alone in this desire, we will include it in one of the next versions.
She is constantly improving
By starting to work in the program now, later you will receive some new functions for product accounting and more conveniences. She herself notifies about the release of new versions and offers to install them. Sometimes these versions contain legislative changes, for example new forms of invoices, payment orders or some other documents.
By downloading the free warehouse program, you will be able to use limited technical support, consisting of consultations on the user forum. And by switching to one of the paid versions, you will be able to use all types of support, including the “Hotline” and the “Remote Support” service. For paid versions it is possible to use the free version after a year.
The free version of Debit Plus can be used by both entrepreneurs and small businesses. The system allows you to maintain warehouse records and includes a system for interacting with customers. The functions of the system include a balance sheet, fixed asset accounting, and wages. The program is available for Windows, Linux, Mac OS.
Free version of the "Debit Plus" system:
- Suitable for both entrepreneurs and small businesses.
- Allows you to maintain warehouse accounting both with and without accounting (at the user's request).
- Works on various OS - Windows, Linux, Mac OS, and DBMS - PostgreSQL, MySQL.
- It is completely ready to work under the conditions of Ukrainian legislation and is promptly updated in connection with its changes.
The system consists of the Eclipse RCP platform, the Debit+ module itself, which is distributed as a compiled jar and configuration.
The entire configuration is written in JavaScript, the forms are in XML. You can use Eclipse for development.
In fact, only one configuration is free - the one with accounting and small pieces of other sections. The rest are paid.
But no one is stopping you from freely modifying it to suit yourself, especially since the site has quite a lot of documentation and examples.
Pineapple. GNU General Public License is a free software license. Software under this license is free for use for any purpose.

Pineapple is a freely distributed accounting automation platform. The system will help automate purchases, sales, and report generation. This free analogue of 1C has distribution kits for Linux and Windows.
Its own technology. The program is free, but the exact license is not known.

"Own technology"- management accounting platform for small and medium-sized businesses. The basic configuration of the system, which meets the requirements of most Russian companies, is distributed free of charge, including for use in commercial organizations. License Agreement and Terms of Use.
Main features:
- warehouse accounting of materials, goods, products;
- accounting and analysis of sales of goods, products, services;
- conducting mutual settlements with customers or suppliers;
- accounting of cash flows at the cash desk, bank, ability to download data from the client bank.
- registration of all necessary primary documents, printed forms that comply with the law;
For all accounting sections, you can generate register statements; in addition, a number of built-in and additional reports are available.
Reports and printable forms can be exported to Excel, Open Office, and also sent by email. It is possible to upload data to accounting programs (if the corresponding additional module is activated).
Benefits of the program:
- High speed thanks to client-server technology
- The network version allows a large number of users to work with a single database, which is unique for free programs of this class
- Multi-company accounting in one database and the ability to work with several databases
- Flexible reports with custom groupings and filters
- Possibility of connecting commercial equipment (RS232 or USB emulation)
- Automatic re-run when correcting old documents
Athena. The program is free, but the exact license is not known.

Purpose:
Development and operation of various accounting tasks (and not only accounting), each of which is created with its own database.
This is a two-in-one system. The developer uses it to build accounting projects, and the user operates the developed projects in it.
The system can be classified as part of the RAD - Rapid Application Development direction, a tool for rapid application development, but on the condition that the developer is not a beginner. The complex, as a tool for developing various accounting tasks, is not so simple. On the pages of this site, beginners will find a lot of information to familiarize themselves with or master the system.
Athena exists in two versions: in the form of single-user and network assemblies.
A project completed using one assembly will work in another.
A few words about the differences between the assemblies are given on the "Download" page.
Athena is distributed free of charge without any conditions or guarantees.
Openbravo. Free ERP system with open source.

Wide, versatile functionality
Rich functional content: End-to-end financial accounting, Sales and CRM, Purchasing, Warehouse, Production, and Project and service management
Built-in extensible environment: Best of Openbravo, third-party modules and vertical solutions for best implementations
Expansion of organizational structure: Simple expansion from a mono-company to a multi-company structure with its own business units and warehouses
Innovative
True open WEB architecture
Ease of use WEB: Simple and secure access to all functionality associated with WEB services, quick integration with other applications.
Easy to change and update: Most unique modifications are done without programming
Deployment flexibility: Mono or multi-company, on Windows or Linux, at home or at a service provider - you choose the ideal conditions
Low cost of ownership
High returns at minimal cost
Minimum initial investment: The “Pay only for services” model reduces the investment burden and allows you to clearly control the cost of the result obtained
Transparent pricing: Simplicity and clarity, no hidden fees, no license overpayments
Quick start, high results: Quick start with initial functionality and inexpensive cost of developing functionality in the future
GrossBee . GrossBee offers its clients a unique opportunity for such systems - to receive a fully functional single-user version of the GrossBee XXI system for free.
The enterprise management system "GrossBee XXI" belongs to the ERP class systems and is designed for complex automation of trading and manufacturing enterprises of various sizes: from corporations to small companies. The system solves problems of accounting and planning of material and financial resources, production, analysis of enterprise performance indicators, and many others.

All functions of the system are implemented as a set of interconnected modules that actively interact with each other and together form a single, holistic application. The modules are replaceable, allowing you to develop customized solutions for specific businesses.
The modules are combined into subsystems, each of which is used to solve specific problems. For example, the material accounting subsystem “deals” with the movement of inventory items, the cash and non-cash accounting subsystem deals with banking and cash transactions, etc.
The structure of the GrossBee XXI system is shown in the figure (click on the corresponding subsystem for detailed information):

GrossBee XXI includes the following main subsystems:
- Material accounting subsystem
- Contract accounting subsystem
- Material resources planning subsystem
- Production accounting subsystem
- Production planning subsystem
- Cash accounting subsystem
- Cash planning subsystem
- Subsystem for accounting for debts and settlements with counterparties
- Fixed asset accounting subsystem
- Accounting subsystem
- Personnel accounting and payroll subsystem
- Economic analysis subsystem
- Enterprise economic monitoring subsystem
- Administrative functions
All subsystems use a common database and exchange information with each other, which makes it possible to create a unified information environment at the enterprise, common to all its divisions. In general, the division into modules is quite arbitrary. For example, the material resources planning subsystem uses both data on the balance of goods in the enterprise’s warehouses and information from the accounting and production planning subsystems, the fixed assets accounting subsystem receives data on equipment wear and tear from the production accounting subsystem, etc.
It should be noted that the system continues to actively develop; new modules and subsystems are constantly appearing in it, which are easily connected to others within the overall system architecture.
VS: Accounting. Accounting module - Free!
VS:Accounting is a program for maintaining accounting records for small and medium-sized enterprises. It allows accounting for organizations with both general and simplified taxation systems.

What is included in the Accounting module:
- General taxation regime and specialized tax regimes of the simplified tax system, UTII.
- Book of accounting of income and expenses.
- Tax return according to the simplified tax system.
- Tax return for UTII.
- Accounting for fixed assets.
- Accounting for inventories and services.
- Accounting for cash transactions and formation of a cash book.
- Accounting for current account transactions.
- Accounting for trade operations in wholesale and retail, accounting for goods at sales prices, calculation of trade margins.
- Accounting for settlements with accountable persons and generation of advance reports.
- Accounting for settlements with counterparties, generation of reconciliation reports.
- Formation of a sales book, a purchase book and invoice journals.
- Formation and uploading of accounting and tax reporting in electronic form.
- Current reporting forms.
- Standard accounting reports: turnover sheet, analytical account and others (with drilling function).
- Different ways of entering transactions: using standard operations, posting documents, manually.
- Client-bank.
Other paid modules can be found at the office. website.
- Salary and personnel
- Personalized accounting
- Trade
- Warehouse
OpenERP.

The system began to develop through the efforts of Fabien Pinckaers in 2000. Tiny ERP soon began to be implemented in the public trading market.
Until the end of 2004, Fabien Pinckaers combined in one person the developer, manager, and distributor of Tiny. In September 2004 (when he completed his research), other programmers were brought in to develop and distribute Tiny ERP.
By 2006, the program was successfully used in specialized bookstores, distribution companies, and service companies.
At this time, the TinyForge resource opens. Since then, developers from all over the world have been involved in the development of modules.
A stable version is released every 4-6 months, and a developer version is released every month. In June 2007, in version 4.1.1, a “web client” appeared, allowing you to use all the capabilities of the system using a regular browser.
In July 2008, Launchpad became the platform for organizing the work of the OpenERP community, and the system itself became more open to translators and developers. Also in 2008, the first version of the OpenERP book was written, replacing the system documentation. Since 2009, OpenERP has been included in the Ubuntu and Debian packages.
Technical features
- Python programming language
- Server-client interaction is implemented using the XML-RPC protocol
- The server part uses PostgreSQL as a DBMS
- GTK-based clients
- Ajax based web client
- A web client has been developed to work using mobile devices (currently access through it is read-only)
- Modular structure
Modules
- Accounting
- Asset accounting
- Budget
- Human Resource Management - HRM
- Products (goods)
- Production
- Sales
- Procurement
- Warehouse management
- SCRUM - project management for software development
- Order lunches to the office
- Project management
Official website of the program: openerp.com
Tria
Standard configurations - free
How Tria works
The Tria platform was created in the image and likeness of the most widespread software product in the vast expanses of the former USSR - 1C Enterprise. Just like 1C, the ready-made solution consists of two parts - a platform (launched application) and a database.
Comparison with 1C or a little history
The Tria system was not born out of nowhere. At first, the developers were creating non-standard solutions based on 1C 7.7. As a result of consistent research, a mechanism for business operations was born.
The essence of this mechanism is that the entire logic of document behavior is not contained in code in a programming language, but is specified using a special reference book Business transactions.
As a result, we received the following advantages:
- The logic of document operation can be changed on the fly, while other users continue to work in the database.
- The process of making changes to the configuration has been significantly simplified and accelerated, and consequently, the cost of support has been significantly reduced. What a programmer does in 1C in a day can be done in TRIA in an hour.
- The level of requirements for the TRIA customizer/implementer has been significantly reduced. People who did not know how to program configured the wiring themselves and radically changed the logic of the program. The emphasis in the requirements for implementers has shifted: first of all, specialists must know the subject area, understand the methodology of work, and only then be specialists in TRIA.
Naturally, Tria turned out to be ideologically similar to 1C. The same hierarchical structure directories, documents, document journals, registers. There is no chart of accounts and periodic details yet - it will be planned over time. Essentially, this is something similar to the “Operational accounting” or “trade” component in 1C.
Here, of course, I would like to draw a comparison table, especially since 1C is familiar inside and out, but many will consider this as anti-advertising. Therefore, we will limit ourselves to a very brief summary: in 1C you can do almost everything that the user wants. The only question is time, money and a good specialist. Our software is more limited in functionality, but everything that can be done in Tria is much easier and faster, and therefore cheaper. At the same time, programming requires a significantly lesser degree of specialist training.
The main competitive advantage is a significant reduction in costs for the purchase, implementation, modifications and IT support of your software.
The configurations offered in TRIA contain all the experience of successfully running the business of our clients. They receive not only the program, but also constant recommendations and suggestions to increase the profitability of their companies. We are proud of the achievements of our clients, that over 4 years of using TRIA in the Lugansk region, not a single client has stopped their business, but on the contrary, despite the crisis, they are successfully developing.
Tria Specifications
For normal operation of Tria, a Pentium 150, 32 megabytes of RAM, and 15 megabytes of disk space are sufficient. The larger the database size and the volume of entered information, the more power the computer (on which the database is located) is required.
The Tria platform is a portable application - i.e. a program that does not require installation. You can install the program by simply copying the entire directory, and carry your accounting on a flash drive. On any computer you can issue documents or receive information about balances.
The free Firebird SQL server is used as a data storage (there are server versions for both Windows and free operating systems (Linux, FreeBSD)).
For single-user work, by default it is proposed to work with the embedded version of the Firebird server, which does not require its separate installation and administration.
You can read more about Firebird's capabilities here:
- www.ibphoenix.com – manufacturer’s website
- www.ibase.ru is the website of the company that took part in the development of this server. Contains a lot of useful information in Russian.
- www.interbase-world.com, www.sql.ru are sites where you can communicate with programmers who operated this server.
Arrival-movement-expense. The module implements a mechanism for documenting inventory operations:
- Accounting for the arrival of goods and materials at the warehouse (division).
- Accounting for internal movement of goods and materials across warehouses and materially responsible persons (MRP).
- Accounting for the write-off of inventory items from a warehouse (division) according to current balances.
Parties. Accounting by batches/series has been set up, which is due to the operating principle of any warehouse.
Storage places. Accounting has been set up for detailed storage locations: Department->Room->Rack->Shelf->Cell
Analogues. A mechanism for forming groups of analogues of inventory items (interchangeable inventory items, equivalents) has been developed - in the nomenclature directory, analogues are easily identified, highlighting the main one in the group. When writing off materials from a file cabinet, it is possible to form a selection taking into account the configured groups of analogues.
Best before date. For each batch of inventory items, you can specify the expiration date. There is a report that shows the stock balances taking into account expiration dates. The user can easily track products that are about to expire.
Certificates. The system allows you to store a list of certificates used, as well as indicate which batch or which inventory item belongs to a particular certificate. You can upload scanned copies of certificates and other files.
Norm and minimum stock. For each material, you can specify its rate and minimum stock in the warehouse (department). Report “Deviation of inventory balances from norms and min. inventory" will allow you to quickly monitor the relevance of remaining materials in the warehouse.
Founding of the parish. In the receipt order document, it is possible to indicate on the basis of which documents (invoice, customs declaration, sales form, invoice, etc.) the receipt of goods and materials was issued. In addition, you can attach files (scanned copies, drawings, etc.) to the receipt order.
Drawings. The material card allows you to enter various additional useful information: files (for example, drawings, images of materials), articles, country and organization of the manufacturer, various data on Russian classifiers.
Quantity 2. Packings. The module allows you to keep track of materials by second quantity and by package.
Barcodes. Accounting for inventory items using a barcode speeds up the work of users and allows you to reduce the number of errors that appear in documents when manually entering information about inventory items.
TSD. To further speed up the program, you can use the data collection terminal; it allows you to remotely generate receipt/movement/write-off documents by reading the list of inventory items and then creating documents in the system.
Relocation requests. These documents are intended for generating inventory requests from departments to the warehouse. On their basis, documents for internal movement are directly generated.
Requests for delivery. These documents are intended for generating requests for inventory items from the supply department to suppliers of inventory items. On their basis, documents for recording inventory items are directly generated.
Requirement for materials. Using the application work scheme, the supply department can use the “Demand for Materials” report, which provides all the information about the needs of departments, warehouse balances, ordered goods, inventory turnover for a specified period. Based on this report, the procurement department can easily determine the need for inventory items for the enterprise.
Integration. The joint work of the “Kontur-Sklad” module with the products of the “Kontur-Accounting” family can be organized in several ways:
- Work on the basis of one single document in the warehouse and in the accounting department, using the ability to collaborate on common documents and customize the individual user interface. Common documents and general reference books are used.
- Work on the basis of separate document registers without intersecting warehouse accounting and accounting. Separate documents and general reference books are used.
- Work on the basis of separate document registers with selective transfer of operations from the warehouse to the accounting department. Separate documents and general reference books are used.
The “Fixed Assets and Intangible Assets” section of the “Tangible Assets Accounting” program provides complete accounting of fixed assets and intangible assets, calculation and recalculation of depreciation for any month an unlimited number of times, revaluation, inventory, and receipt of output forms for any period.
When implementing the task, the directories are filled in: chart of accounts, clients, depreciation transactions, depreciation calculation methods, directory of financially responsible persons, directory of precious metals.
· The chart of accounts directory describes the structure of the chart of accounts, i.e. the accounting scheme is determined. The directory contains a list of all accounts and items of analytical accounting. For this task, the chart of accounts looks like this:
|
Name |
|
|
Fixed assets |
|
|
Fixed assets of the main activity |
|
|
Industrial buildings |
|
|
Facilities |
|
|
Power machines and equipment |
|
|
Working machines and equipment |
|
|
Computer Science |
|
|
Other machines and equipment |
|
|
Vehicles |
|
|
(except furniture) |
|
|
Library fund |
|
|
Fixed assets of other industries producing goods |
|
|
Facilities |
|
|
Power machines and equipment |
|
|
Working machines and equipment |
|
|
Measuring and control instruments |
|
|
Computer Science |
|
|
Other machines and equipment |
|
|
Vehicles |
|
|
Industrial and household equipment |
|
|
Productive livestock |
|
|
Fixed assets of other industries providing services |
|
|
Fixed assets of other industries, rendered. conventional (except for residential buildings) |
|
|
Facilities |
|
|
Power machines and equipment |
|
|
Working machines and equipment |
|
|
Measuring and control instruments |
|
|
Computer Science |
|
|
Other machines and equipment |
|
|
Vehicles |
|
|
Industrial and household equipment |
- · The clients directory contains a list of all accounting entities: our organization, including branches, divisions, employees, third-party organizations participating in economic turnover. Each client has its own unique code (the program controls this condition).
- · The depreciation postings directory contains a list of postings for accrual of depreciation of fixed assets by departments and l.o.l. Specify the balance sheet account for accounting for inventory numbers for which depreciation will be calculated, M.O.L. code, department code, debit account and credit account for recording depreciation transactions. All transactions are recorded in the ledger.
- · The reference book describes methods for calculating depreciation of fixed assets.
[ 0 ] - depreciation is not accrued
[ 1 ] - according to the annual depreciation rate:
Depreciation = Book value*standard/100/12
[ 2 ] - monthly norm, count. months
[ 3 ] - by motor rally:
Depreciation=Book value*Mileage/1000*Normal/100
[ 4 ] - by production volume:
Depreciation=Book value*Amount of work*Normal/100
[ 5 ] - by service life, months
[ 6 ] - according to the write-off act, % of the initial write-off
[ 8 ] - by service life, months (100%)
[ 9 ] - at per ton rate
[ 11 ] - according to the annual depreciation rate from the residual value:
Depreciation=Residual value*Normal/100/12
Depreciation=Book value*Normal/100
This company uses 0, 1 and 3 wear methods. The depreciation method is assigned to each inventory item. Used when calculating depreciation of fixed assets.
- · The directory of financially responsible persons is not adjusted by users; it is generated automatically from the directory Clients based on the criterion mol-1. Used when entering documents and printing output forms.
- · The precious metals directory indicates the code of the precious metal and its name.








 About the company Foreign language courses at Moscow State University
About the company Foreign language courses at Moscow State University Which city and why became the main one in Ancient Mesopotamia?
Which city and why became the main one in Ancient Mesopotamia? Why Bukhsoft Online is better than a regular accounting program!
Why Bukhsoft Online is better than a regular accounting program! Which year is a leap year and how to calculate it
Which year is a leap year and how to calculate it